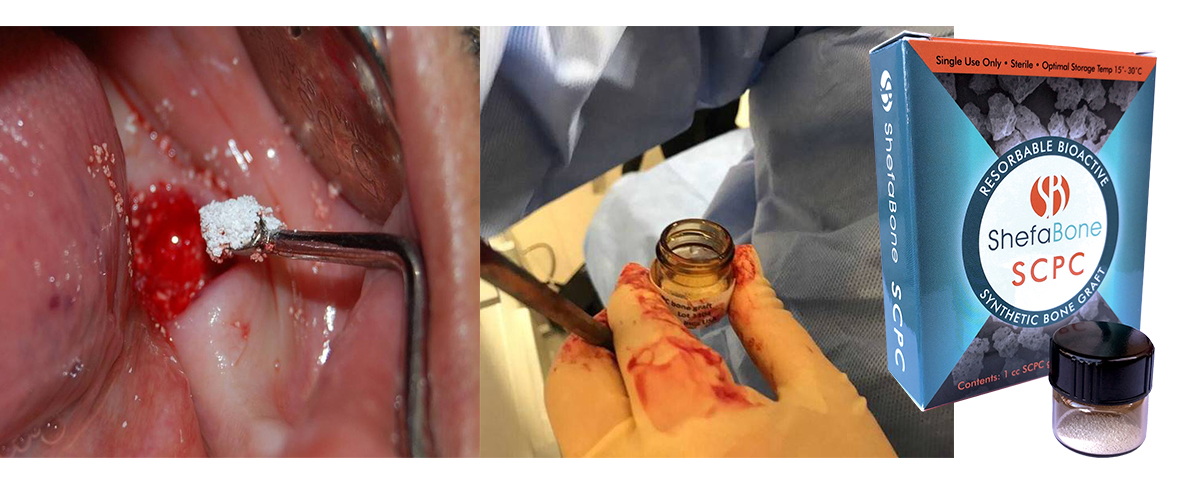
Socket Augmentation
Case Study 1
Treatment of periodontal defect
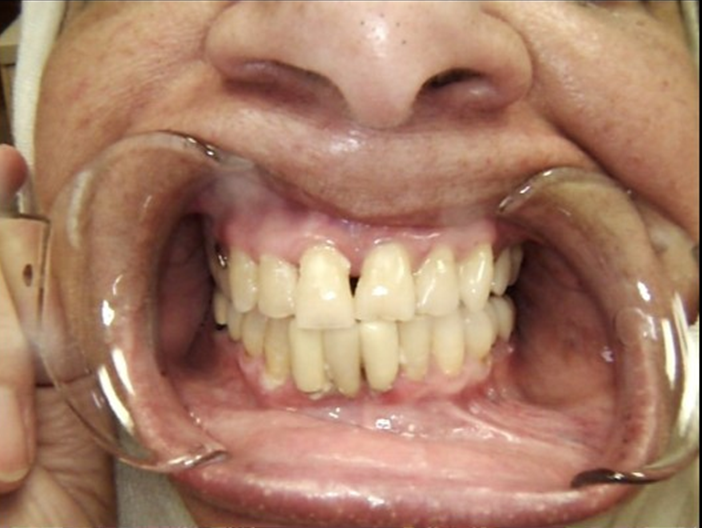
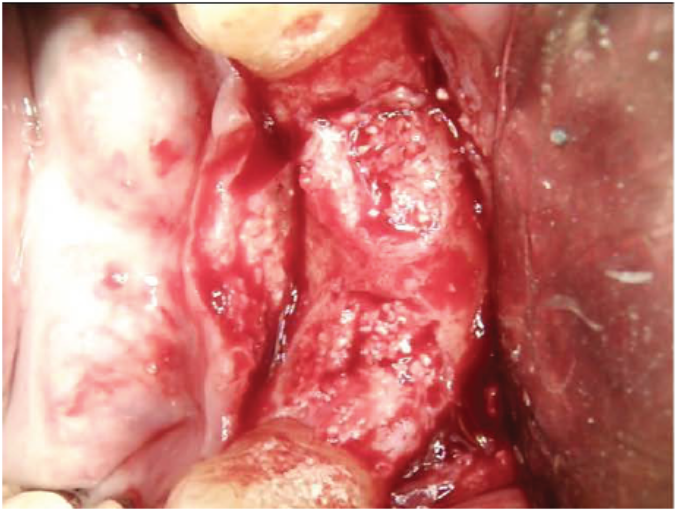
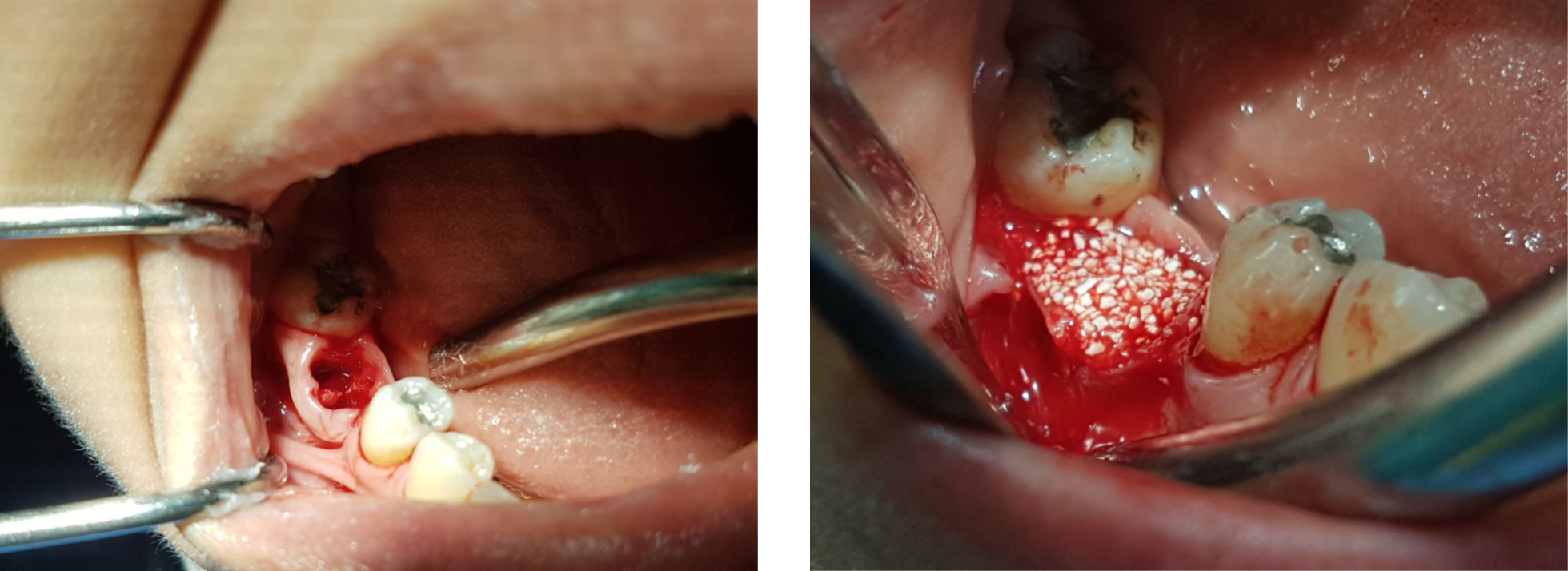
Clinical view shows gingival inflammation and suppuration area tooth #26
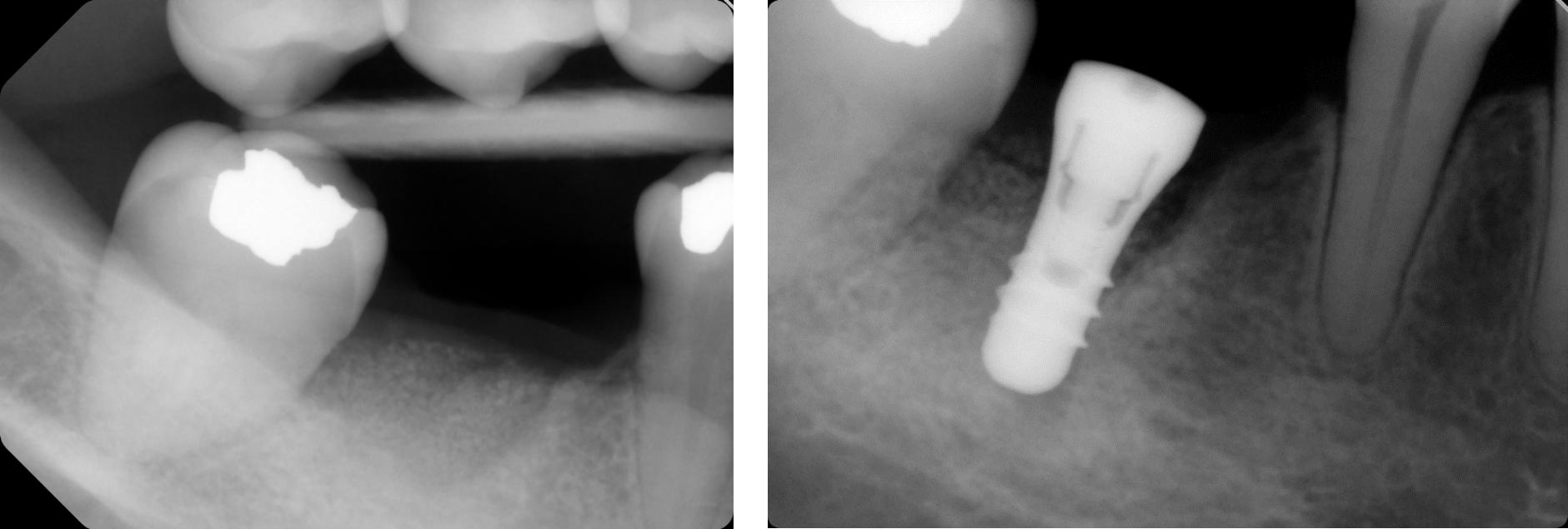
Periapical radiograph showing large bone defect around root # 26
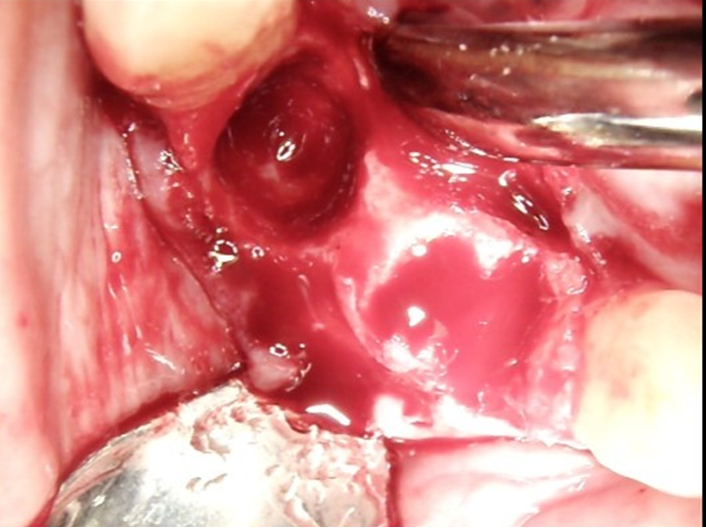
Clinical view of the surgical site after reflection of the flap
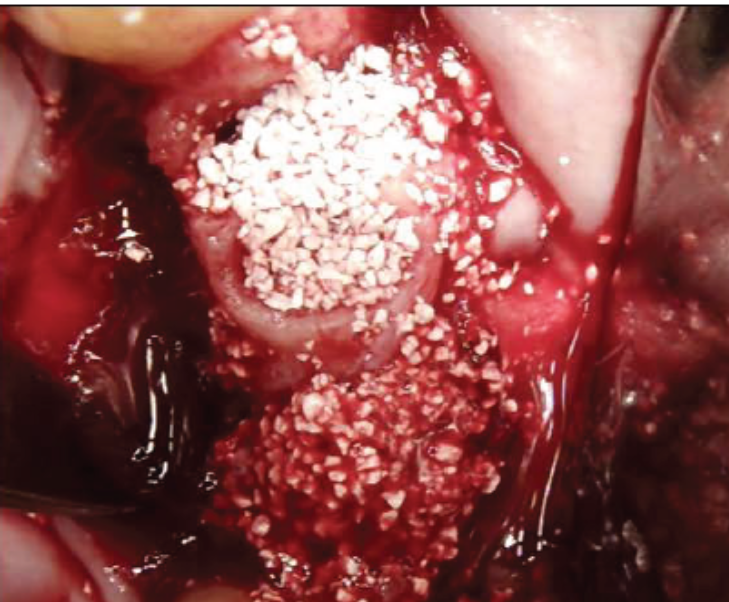
Clinical image showing SCPC granules packed in extraction sockets # 23 and 24 as well as in the large defect area in site 26 in an attempt to fill in bone and rebuild the vertical bone height in site 26.
3 months postoperative Evaluation of bone filland SCPC resorption
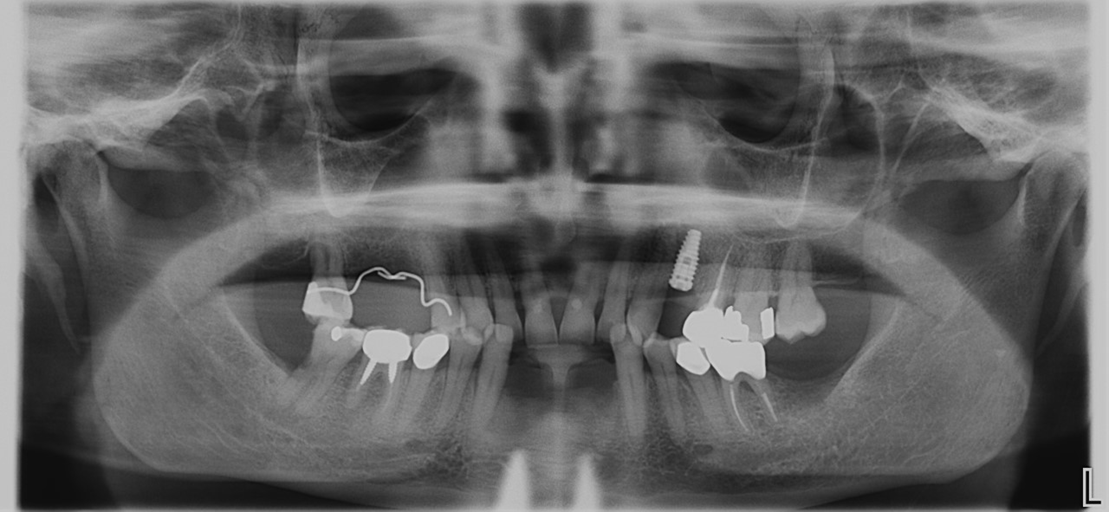
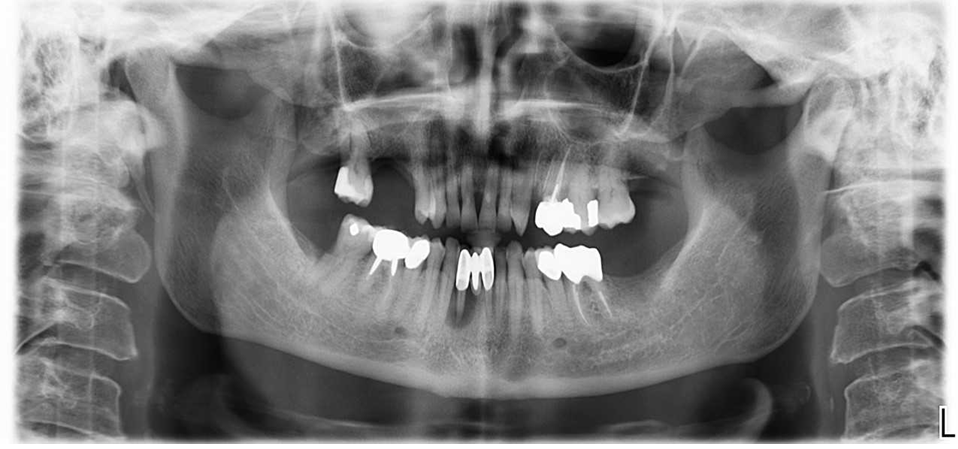
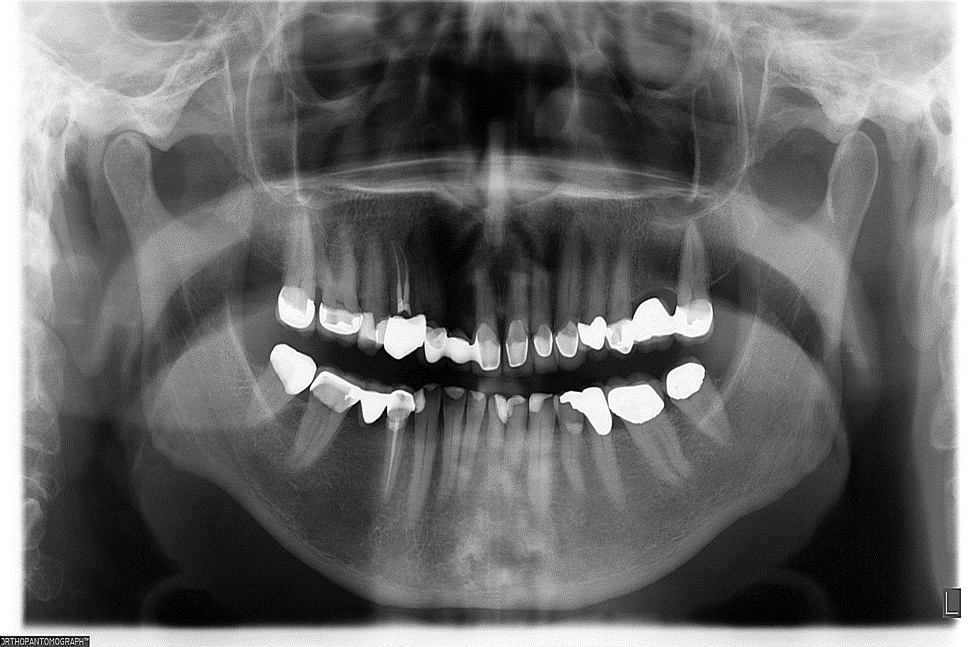
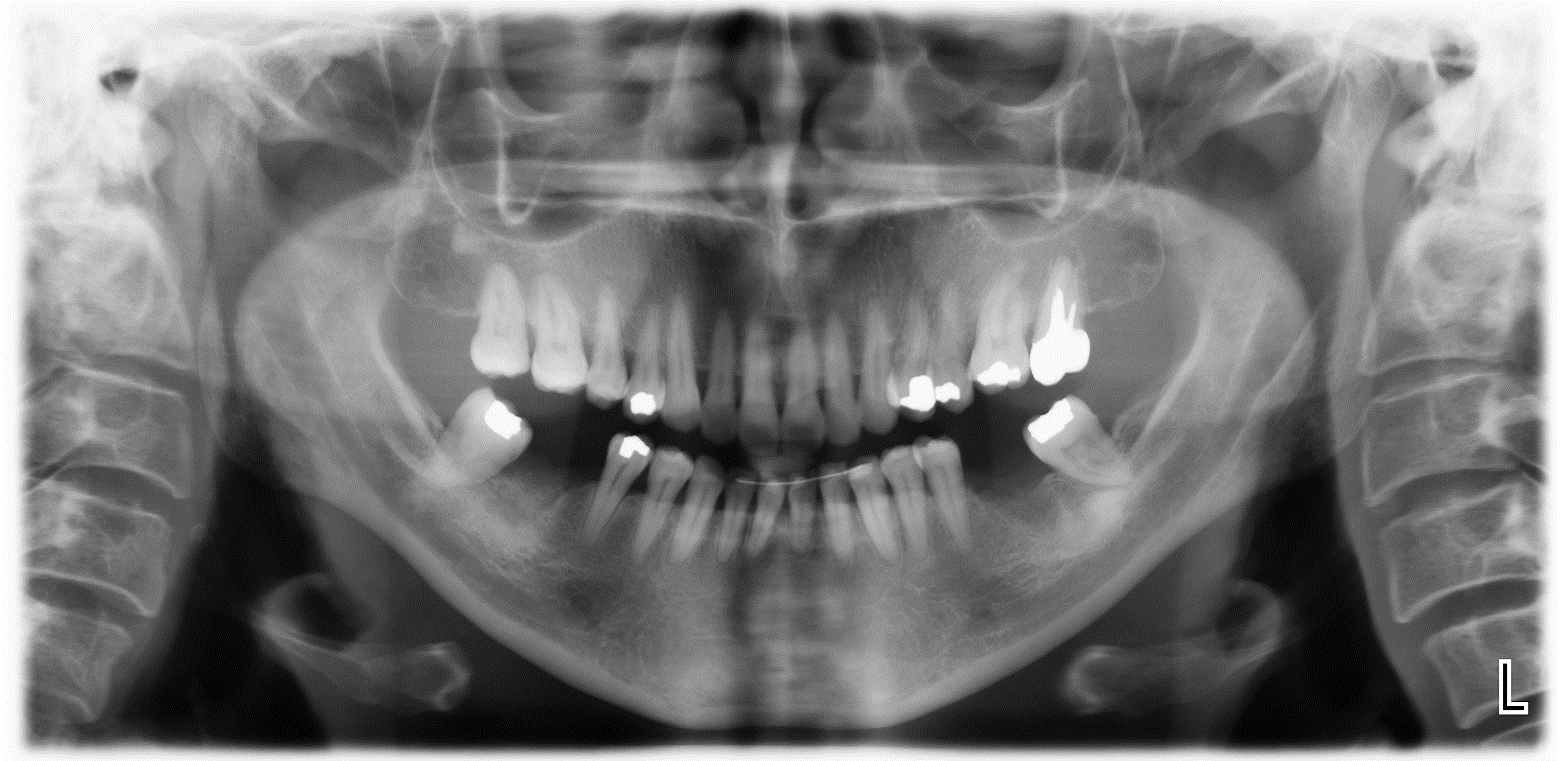
Panoramic X-ray showing complete bone fill in sites # 23, 24 and 26 after three months healing time.
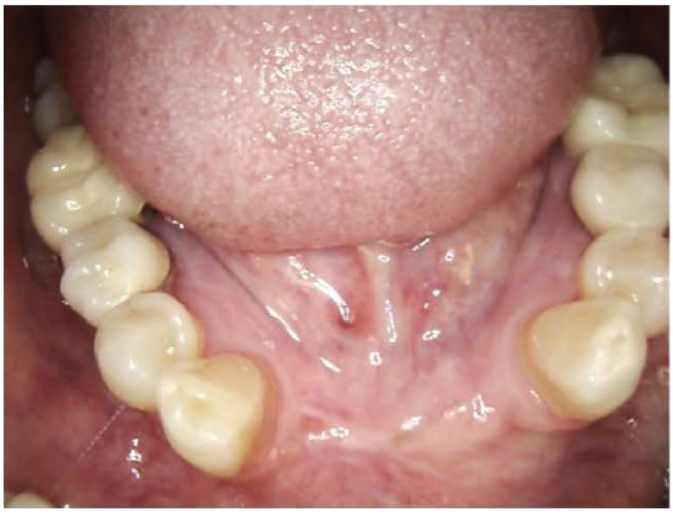
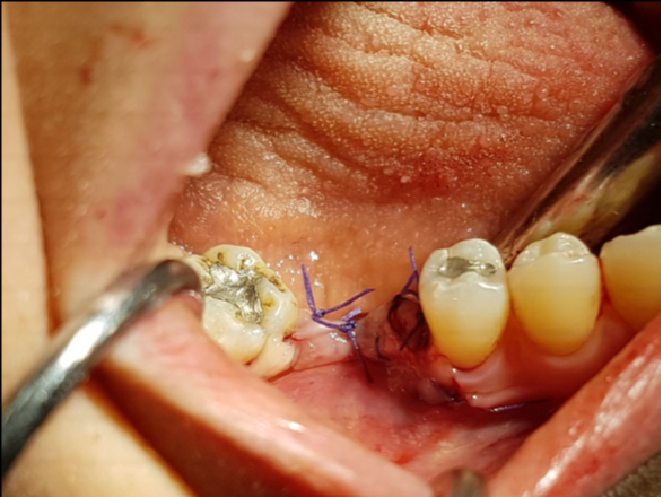
Clinical image of the grafted site after 3 months of healing before flap reflection and implant placement
Clinical image showing the grafted sites after 3 months. The defects were completely filled with new mature bone.
The high quality and complete fill of mature bone in the large defect grafted with SCPC granules after 3 months healing allowed for satisfactory implant stability. SCPC granules have a strong stimulatory effect on bone cells and induction of new bone formation. New bone formation was associated with graft material resorption.
Case Study 2
A 65 years old healthy white Caucasian female came with Broken bridge and sever decay of tooth #6
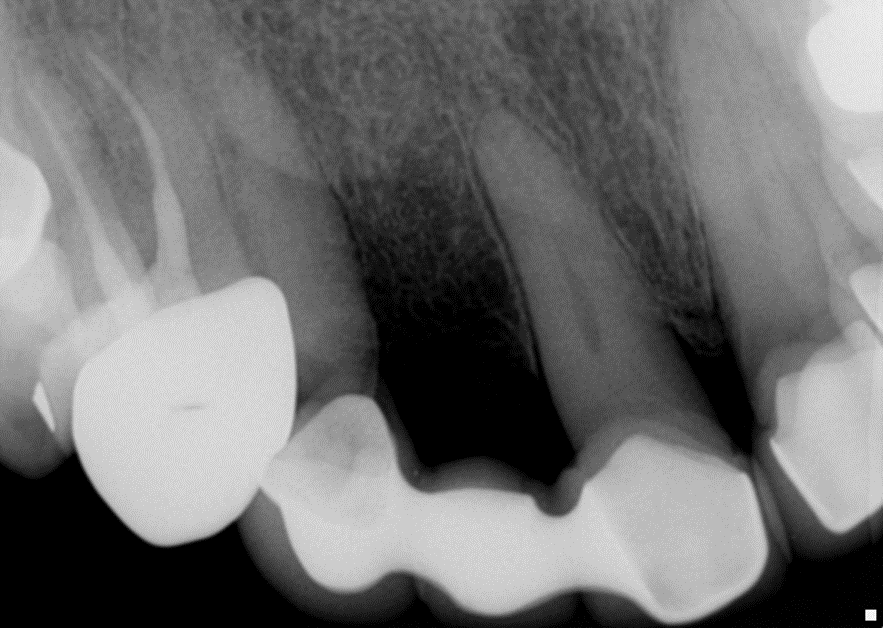
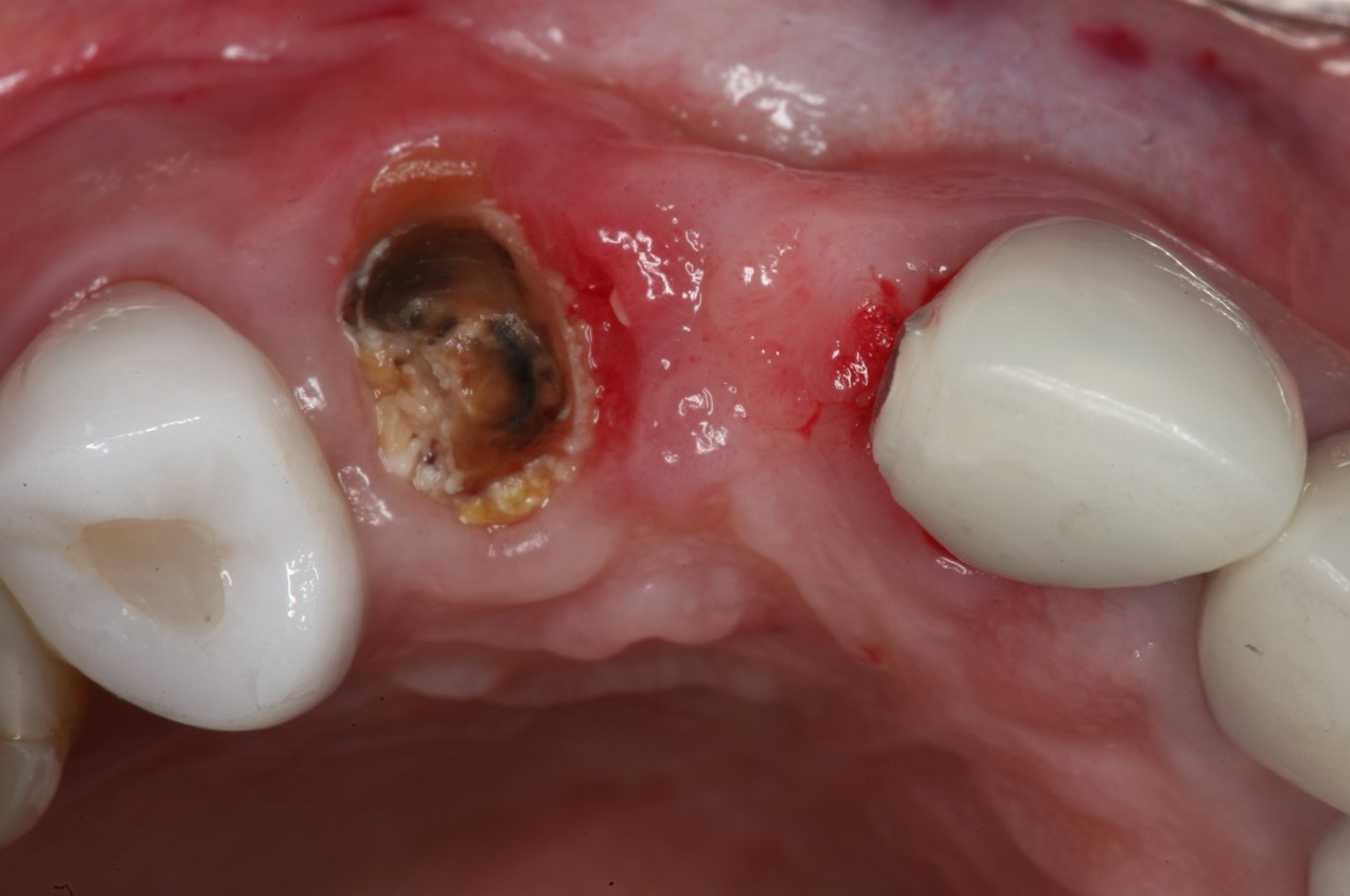
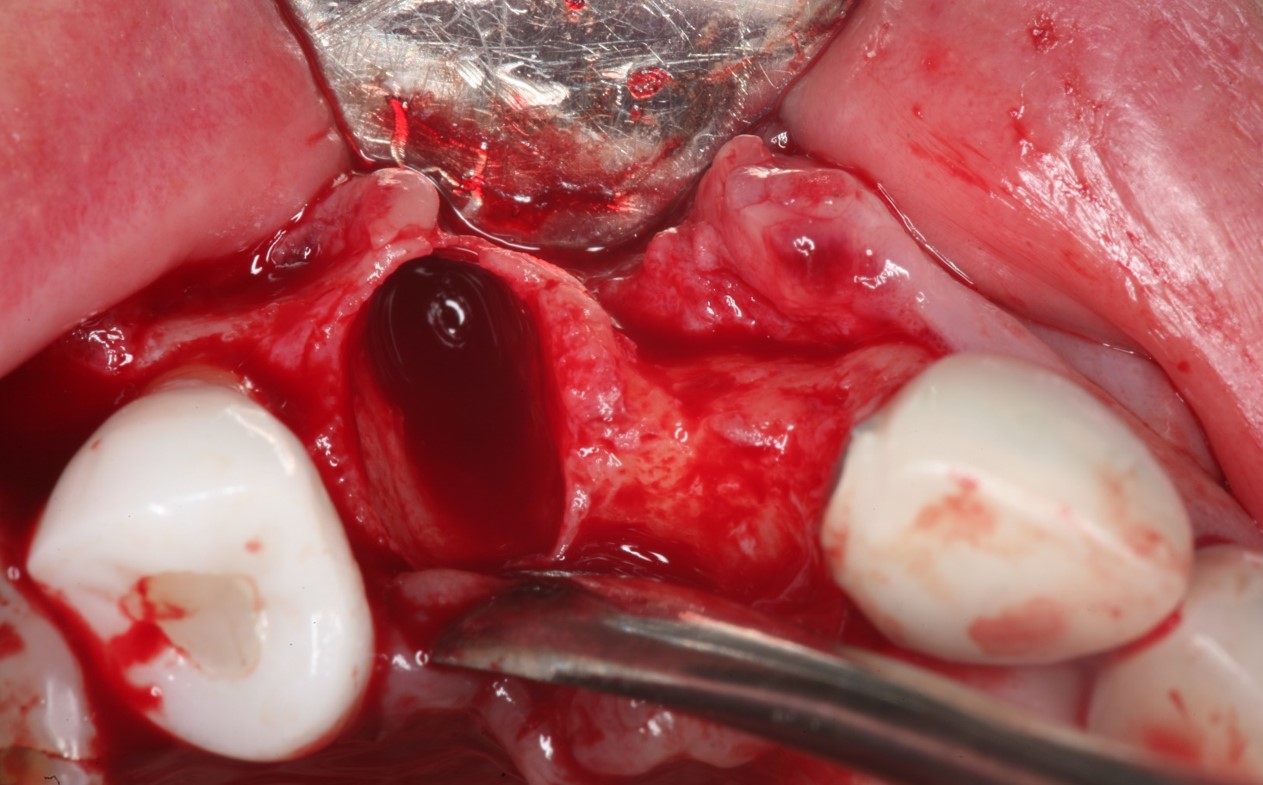
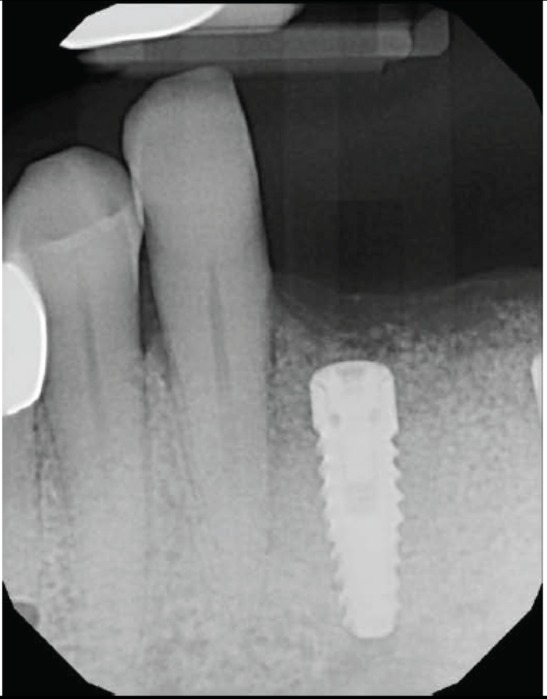
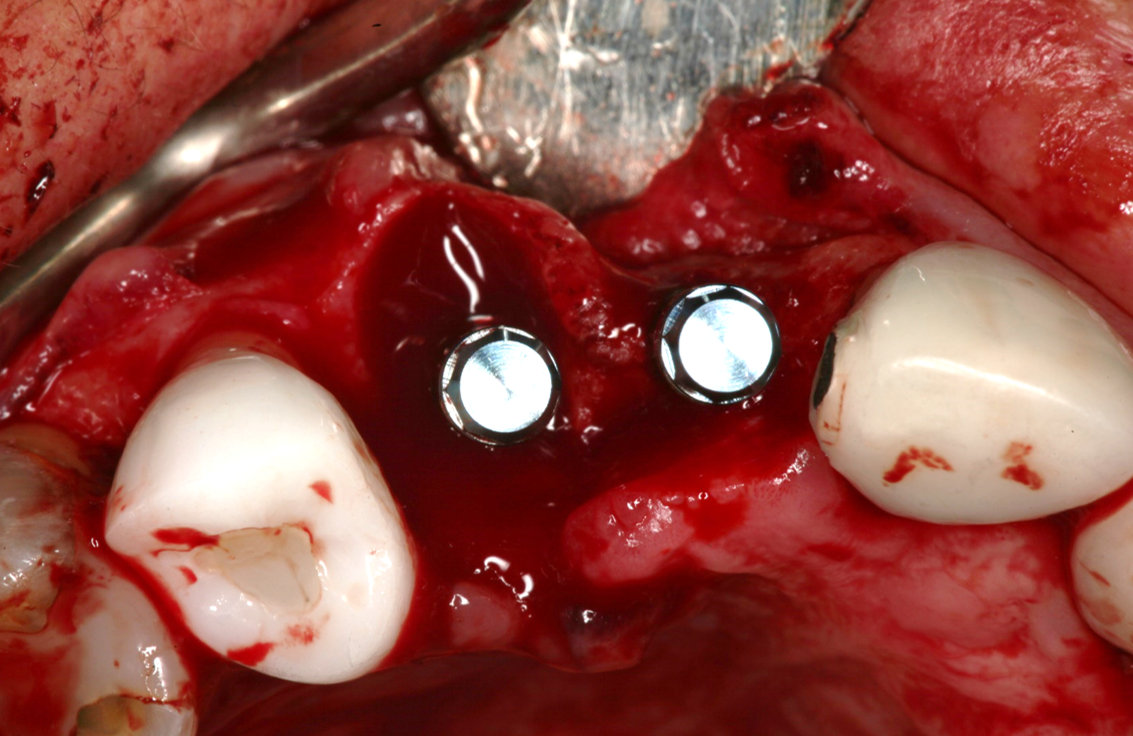
Two implants were inserted in tooth #6 and #8. The graft is packed in the jumping distance between the implant surface and internal socket wall.
SCPC granules were soaked in sterile saline for 5 min before grafting.
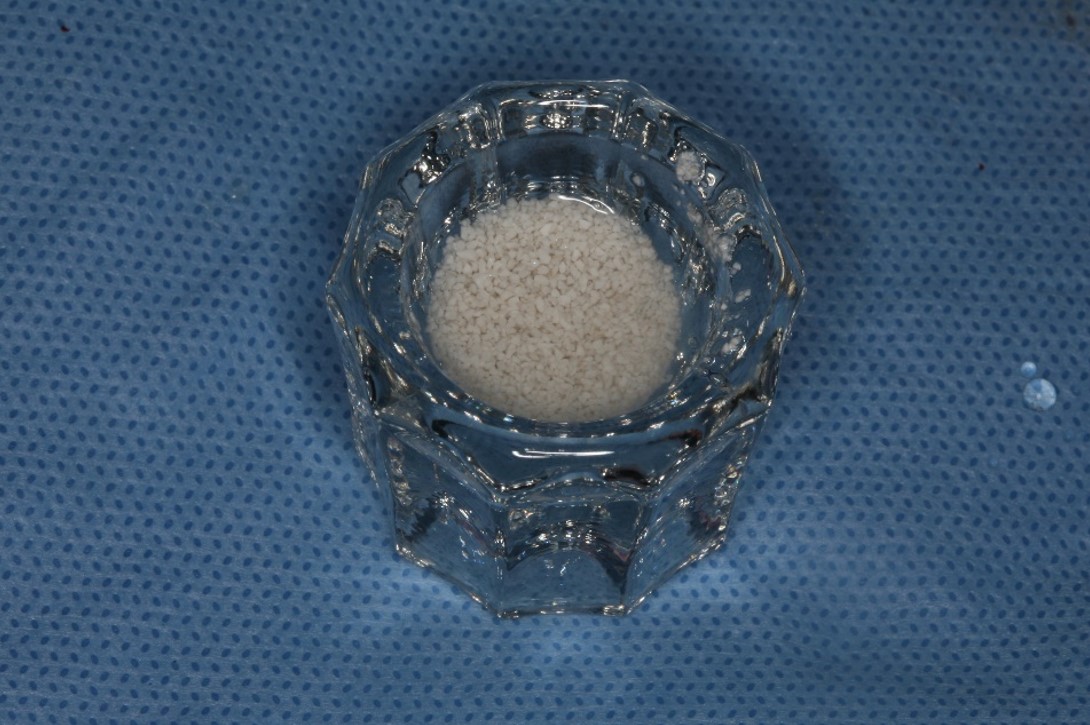
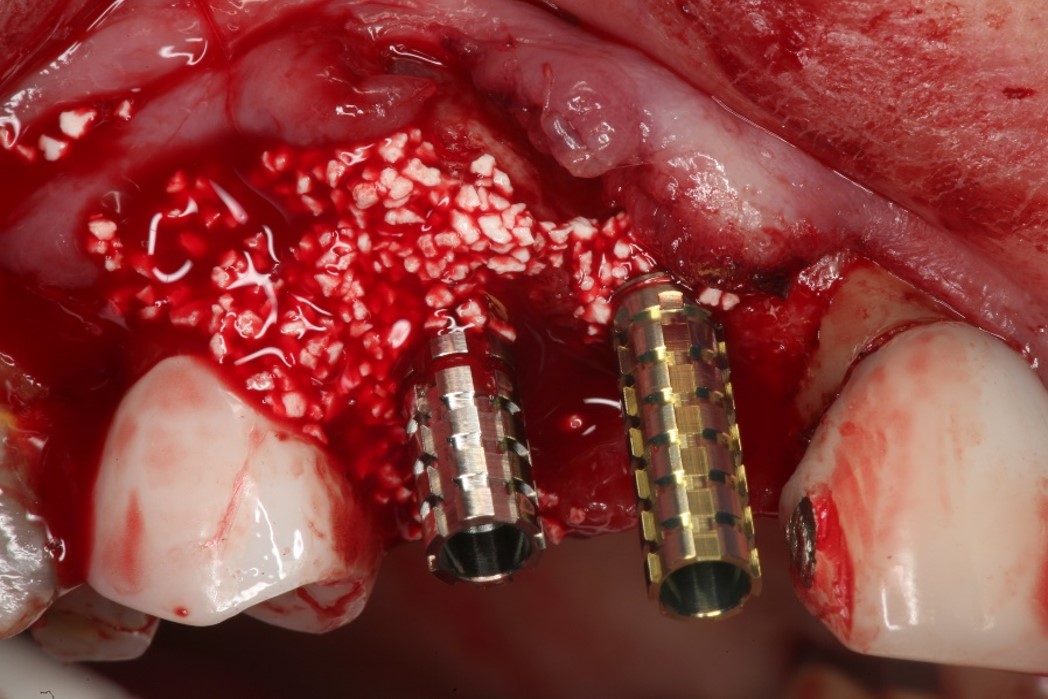
- SCPC particles were grafted around the two implants.
- The SCPC graft is packed in the jumping distance between the implant surface and internal socket wall.
- And SCPC was also placed on the ridge to increase the thickness of the ridge.
Immediate Temporization:
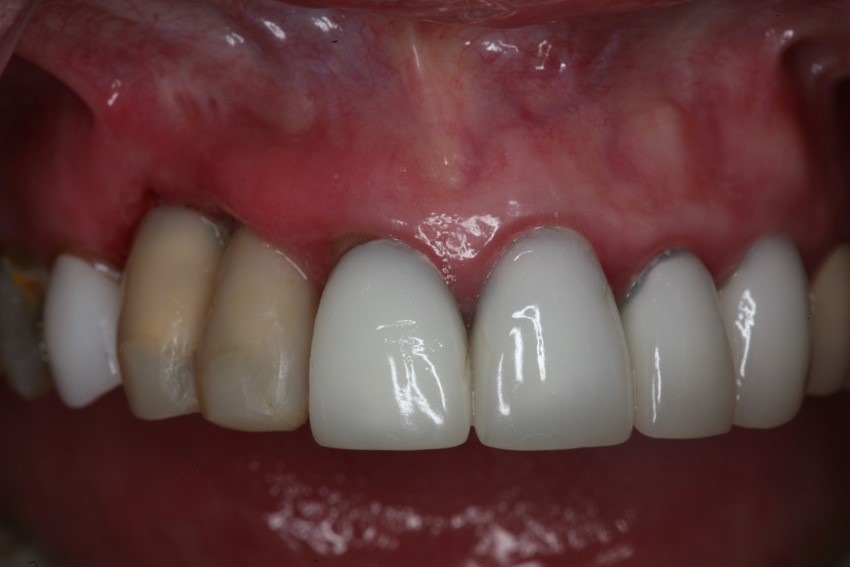
Adequate bone formation around the implant. Stable bone crest:
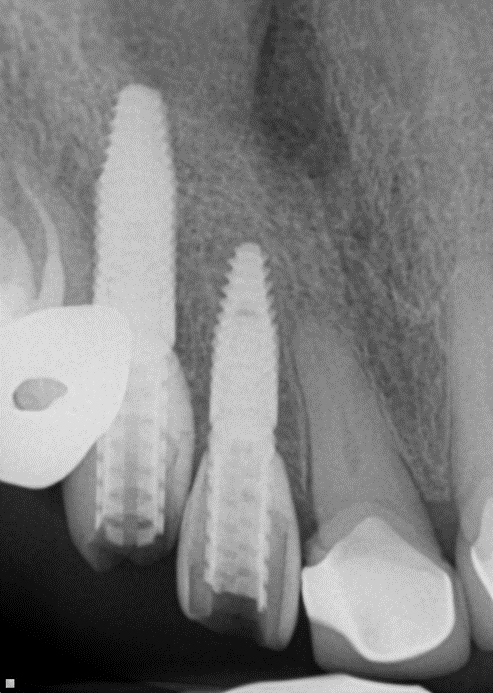
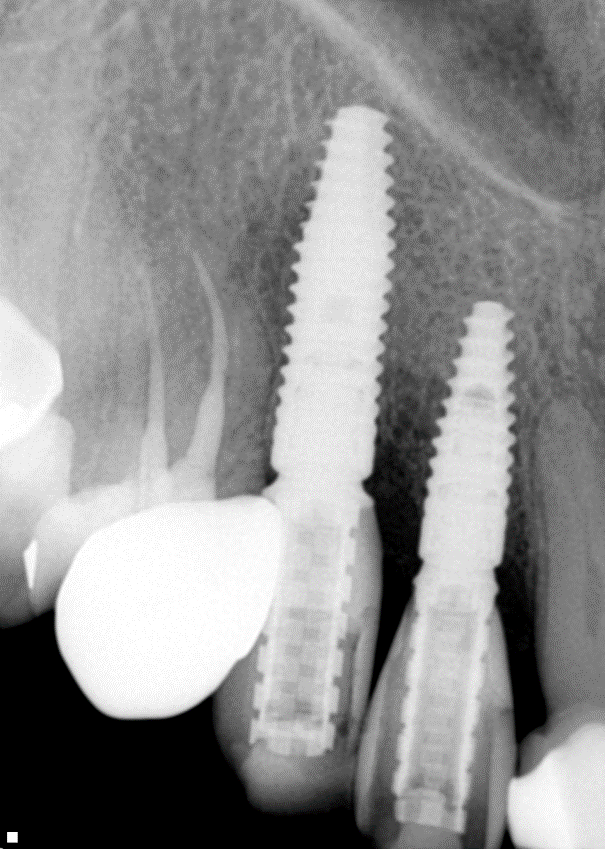
Case Study 3
Extraction of upper left maxillary molars (#14 and #15) in a 65 year old healthy white Caucasian female.
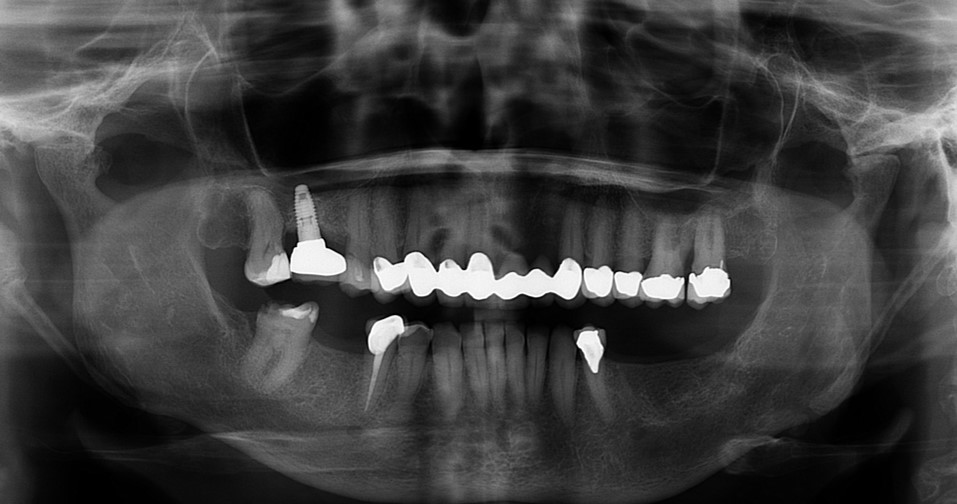
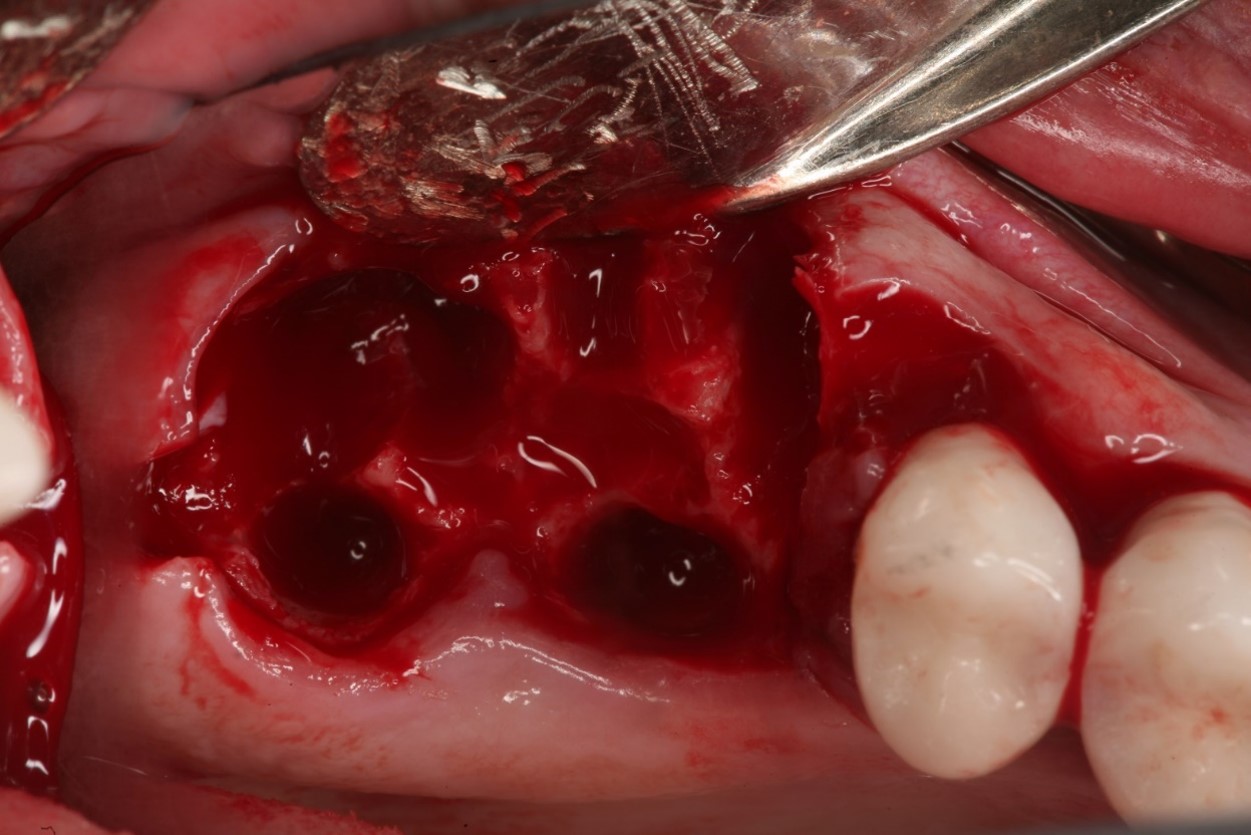
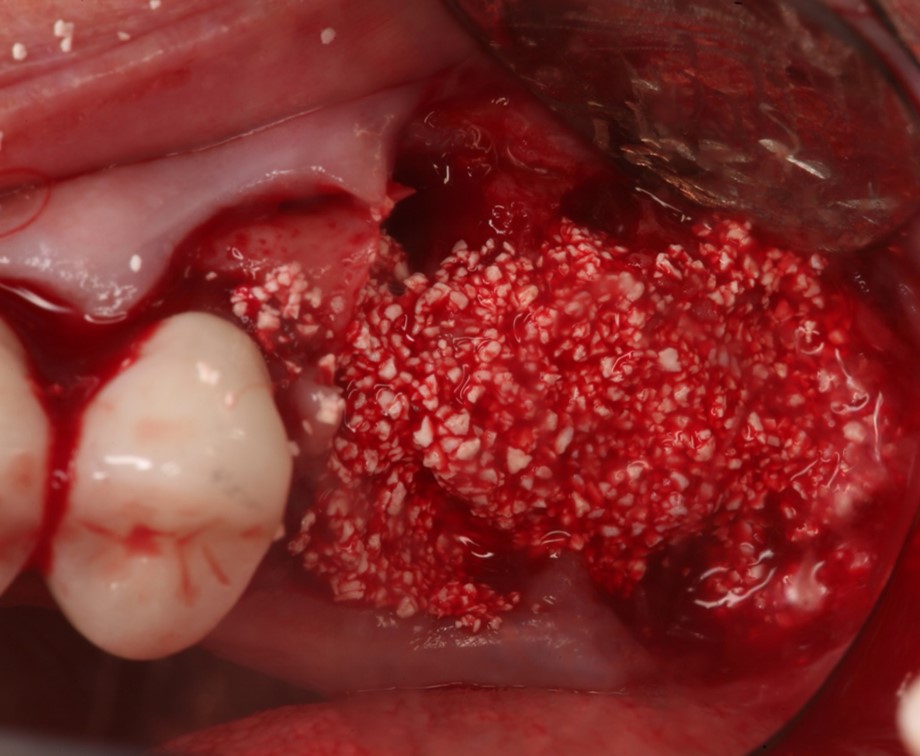
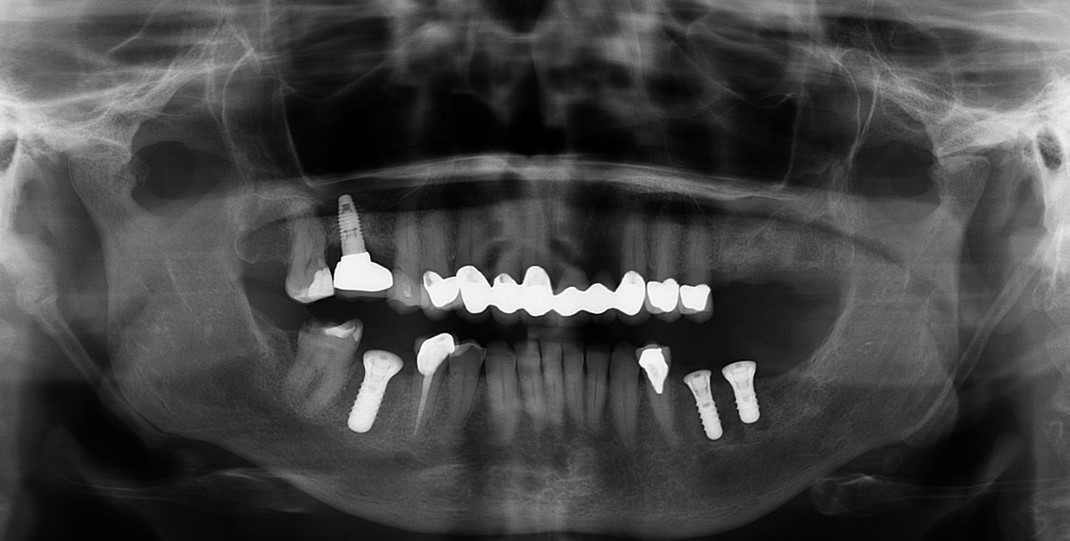
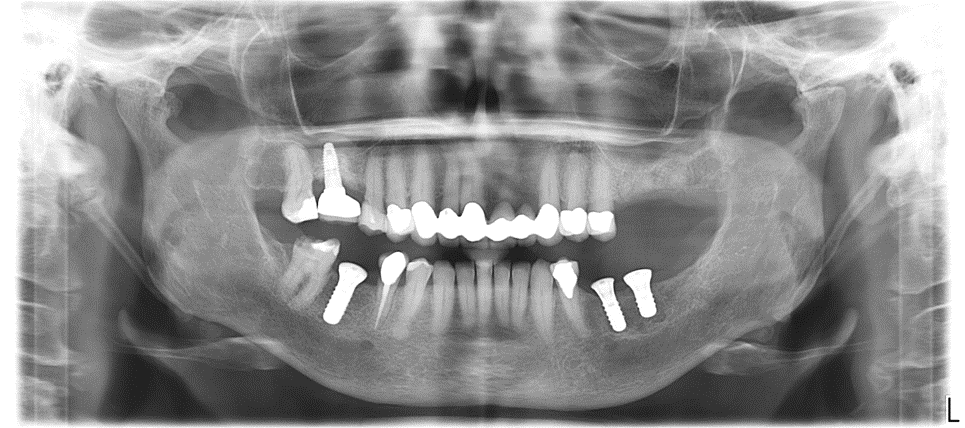
Case Study 4
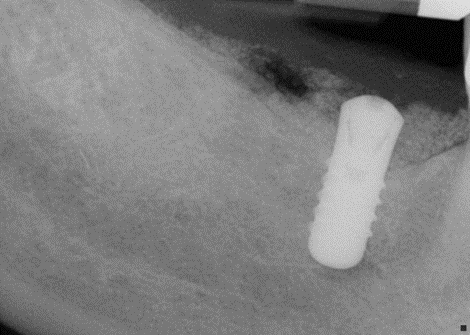
Ridge augmentation at the time of implant placement in Caucasian Male
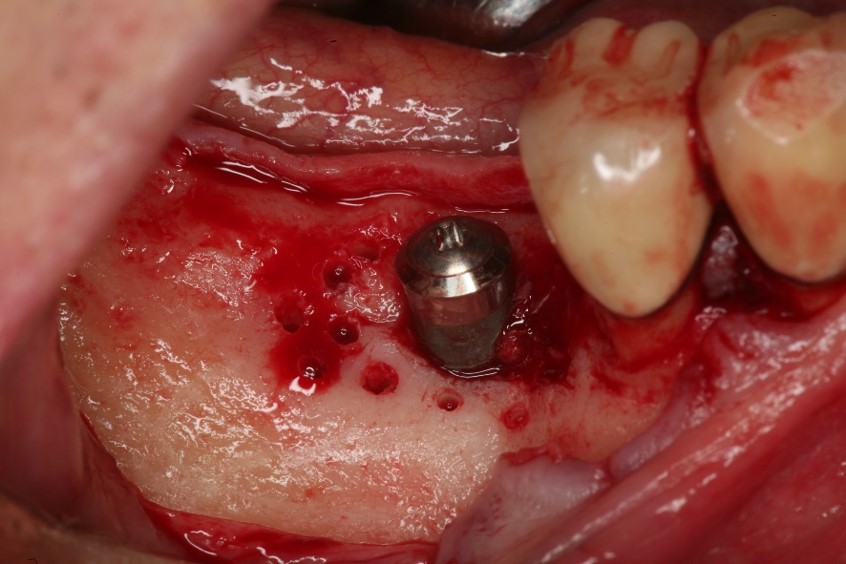
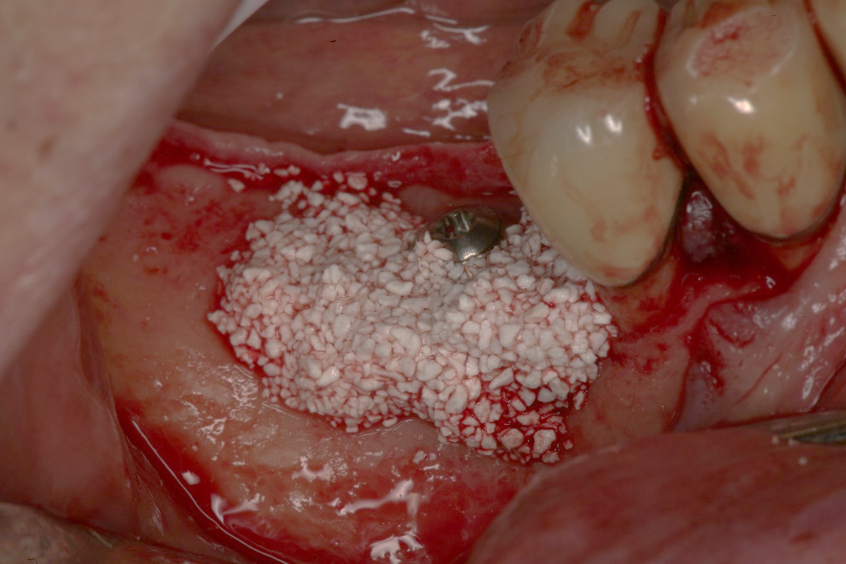
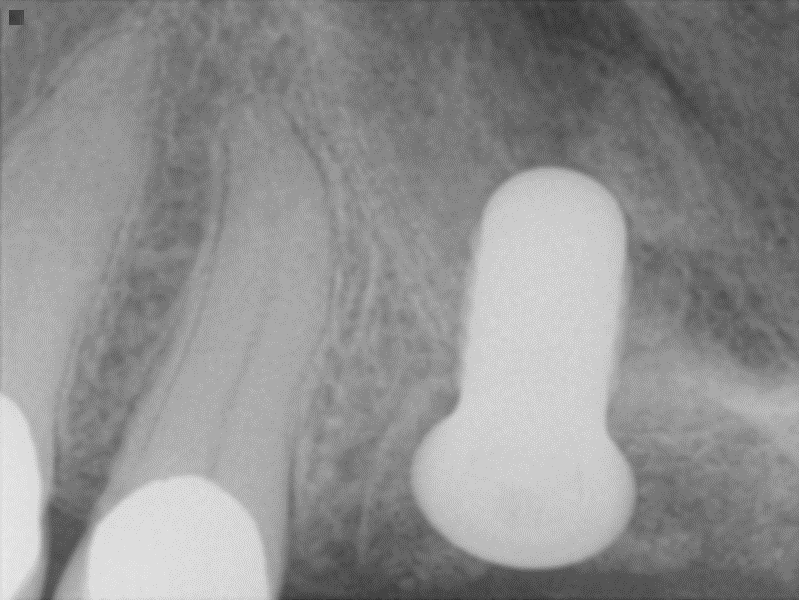
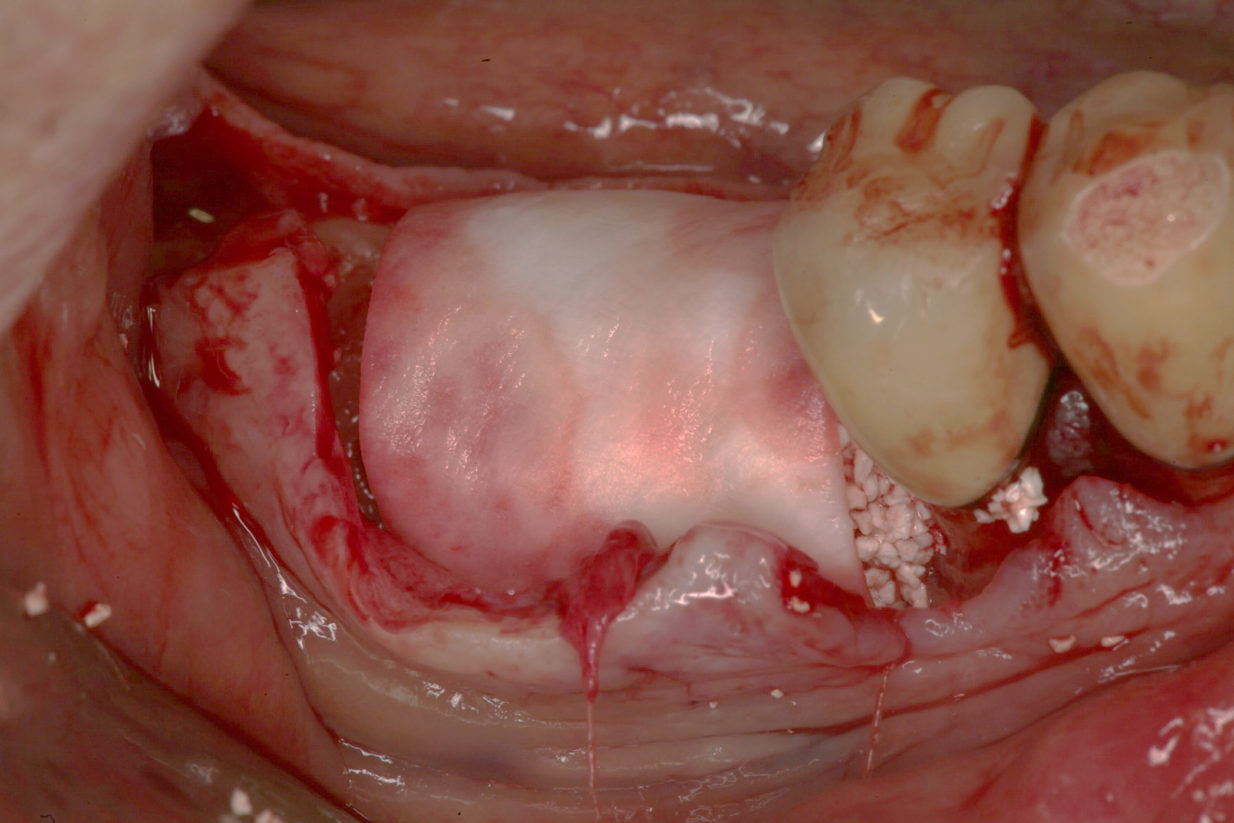
- Site #30 needed an implant, but the site does not have enough width (the buccal lingual width is small)
- After flab reflection, the site did not have enough bone in the buccal lingual width, so the plan was to place an implant and perform bone graft at the time of implant placement.
- (left) the implant was placed and the ridge was prepared for bone grafting where decortication was made to facilitate blood supply and bone cells contact with the SCPC.
- (Right) SCPC bone graft in place- implant can be seen in place
Case Study 5
Socket Preservation in 24 year old male who has a perforated Root canal on #8.
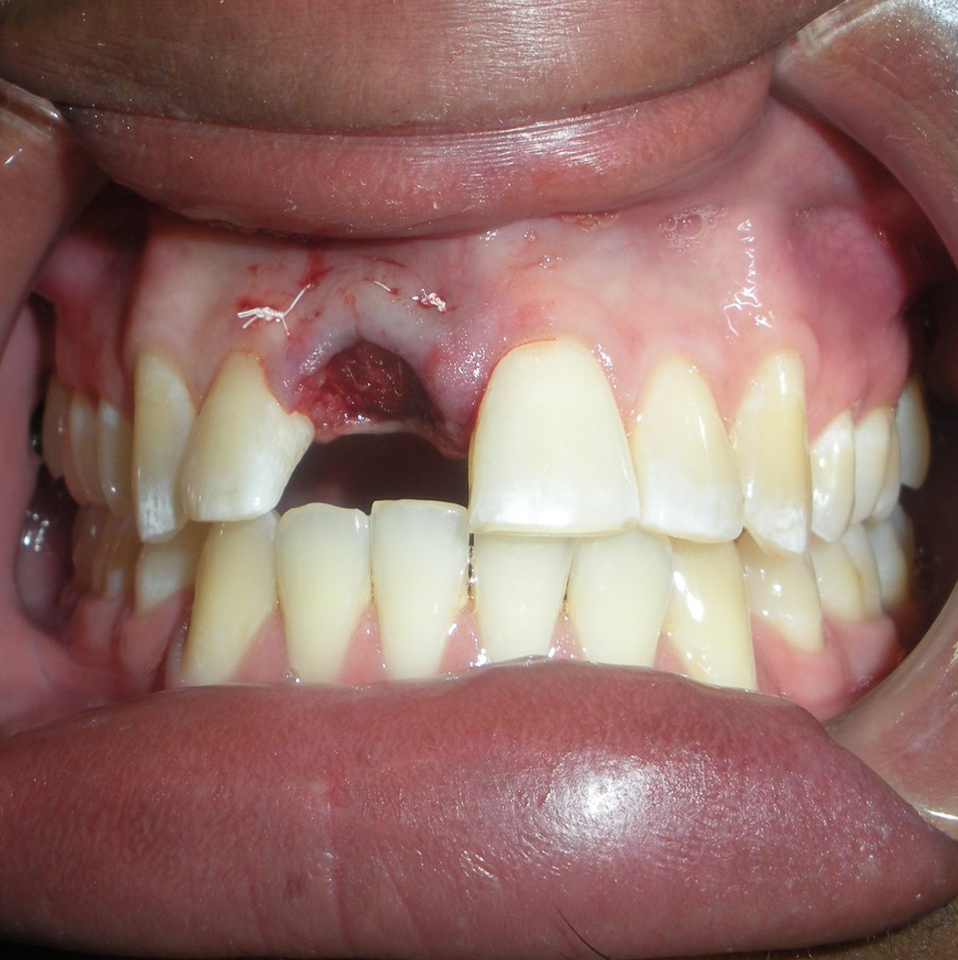
- After tooth removal, the socket was immediately grafted with SCPC bioceramic granules. The SCPC granules were applied dry and loosely packed. The blood inside the socket wetted the SCPC granules
- A resorbable collagen cellulose fibers (sure-stop), that transform into gel in contact with blood, was placed on the top of the SCPC granules.
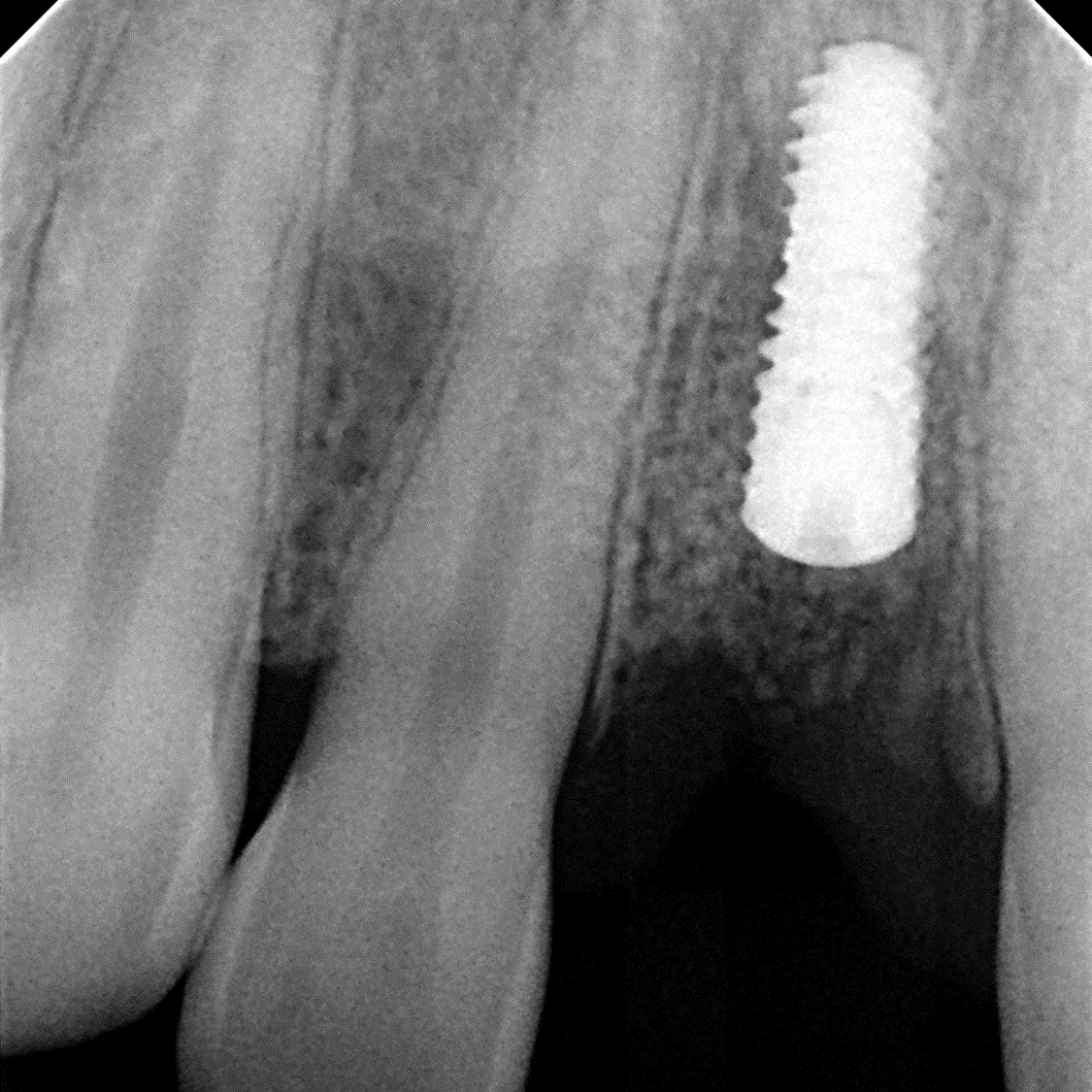
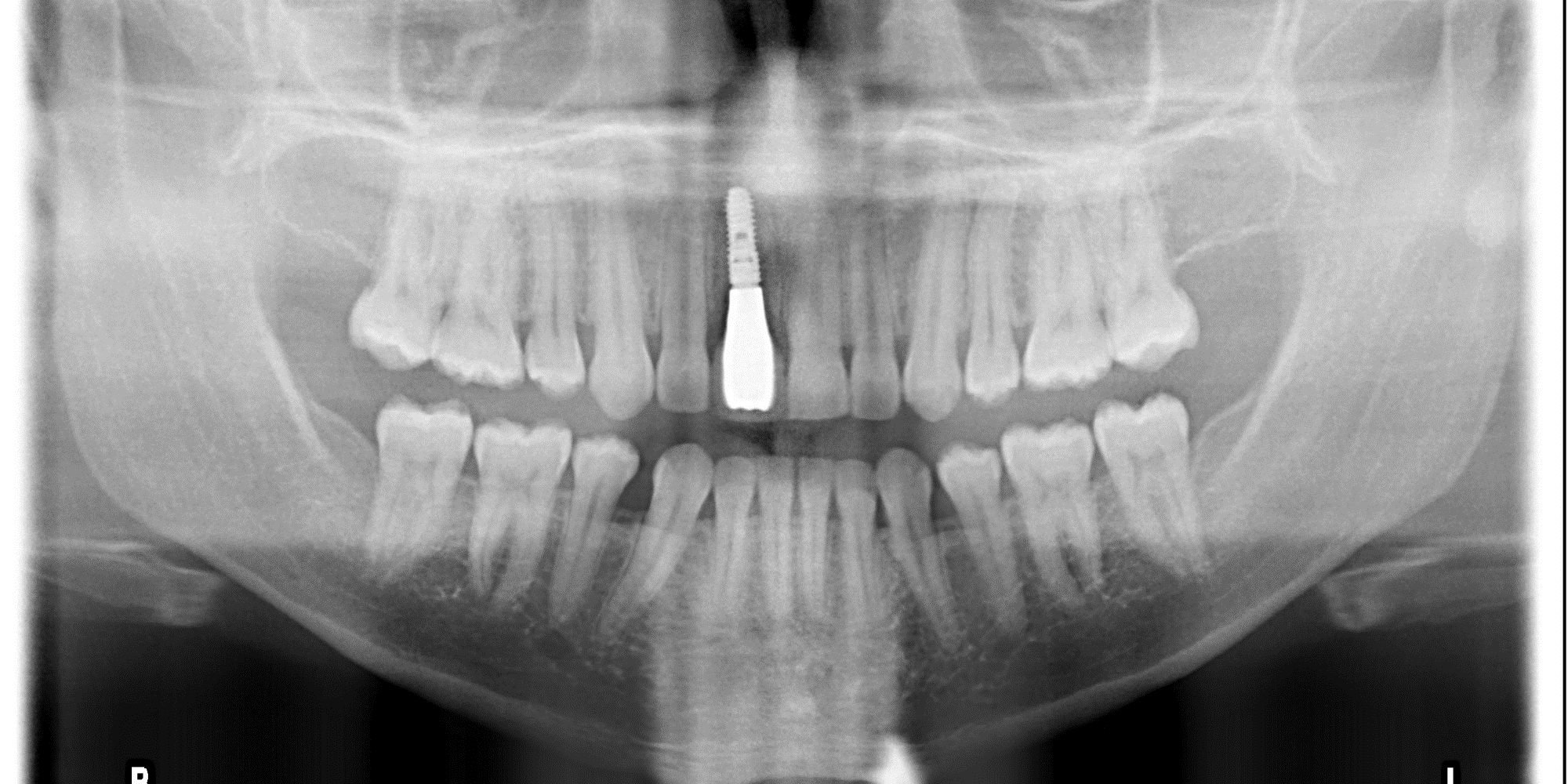
Case Study 6
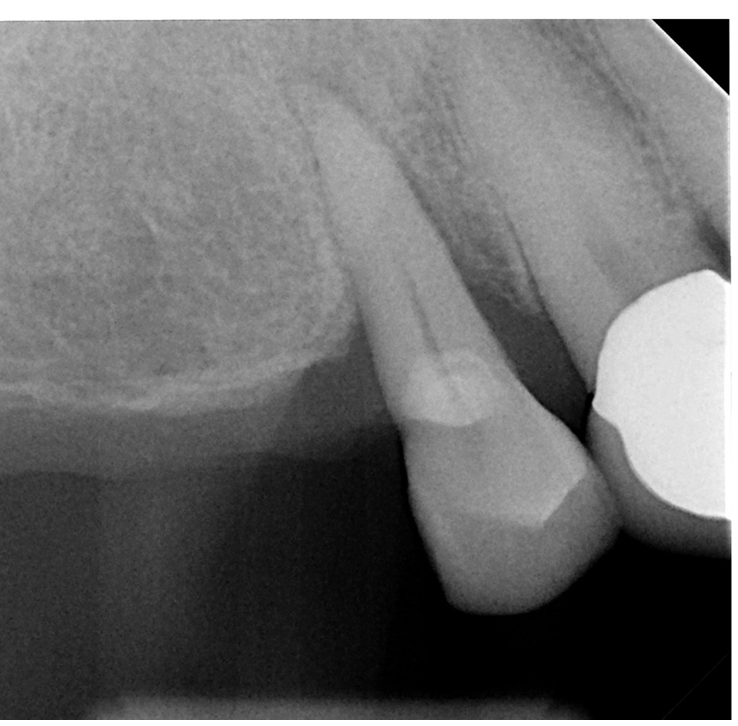
- 63 yo, female, has no medical conditions or medications
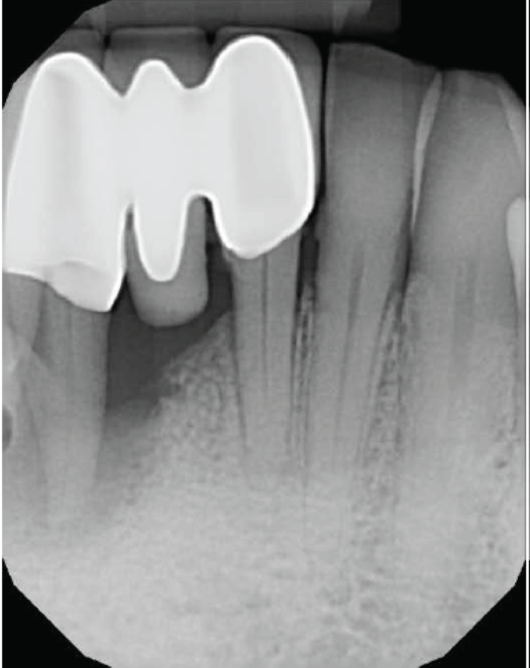
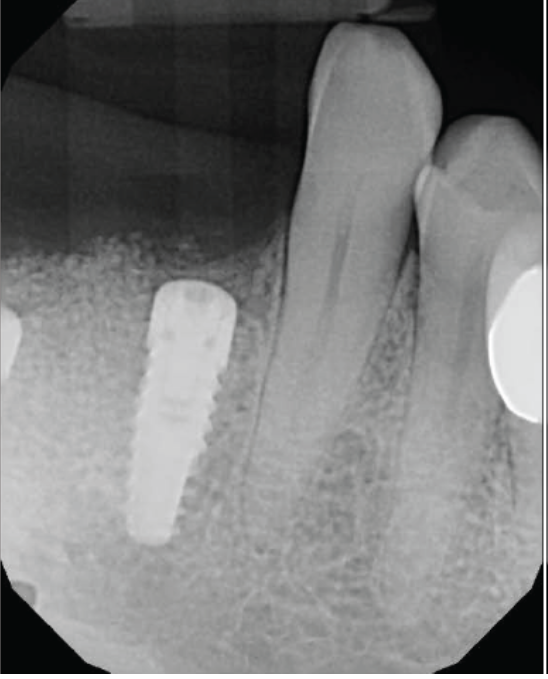
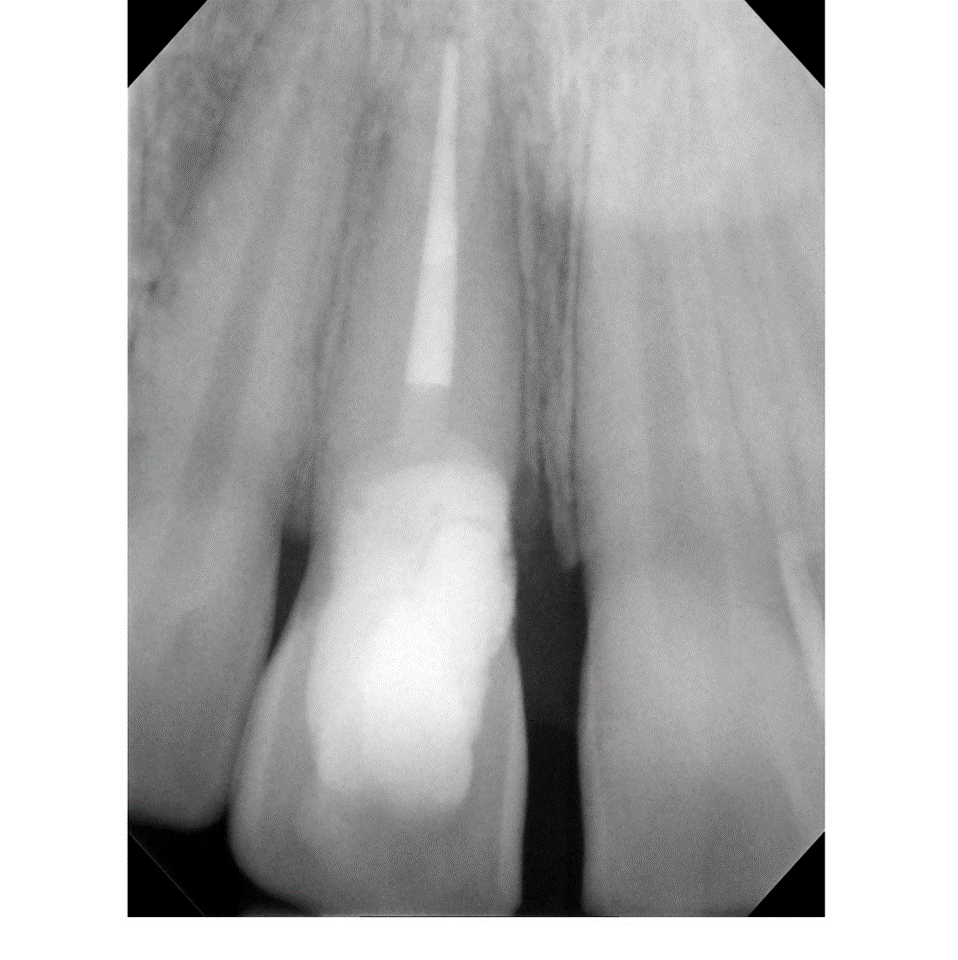
- Preoperative radiograph tooth # 5
- Localized sever chronic periodontitis (class 3 mobility)
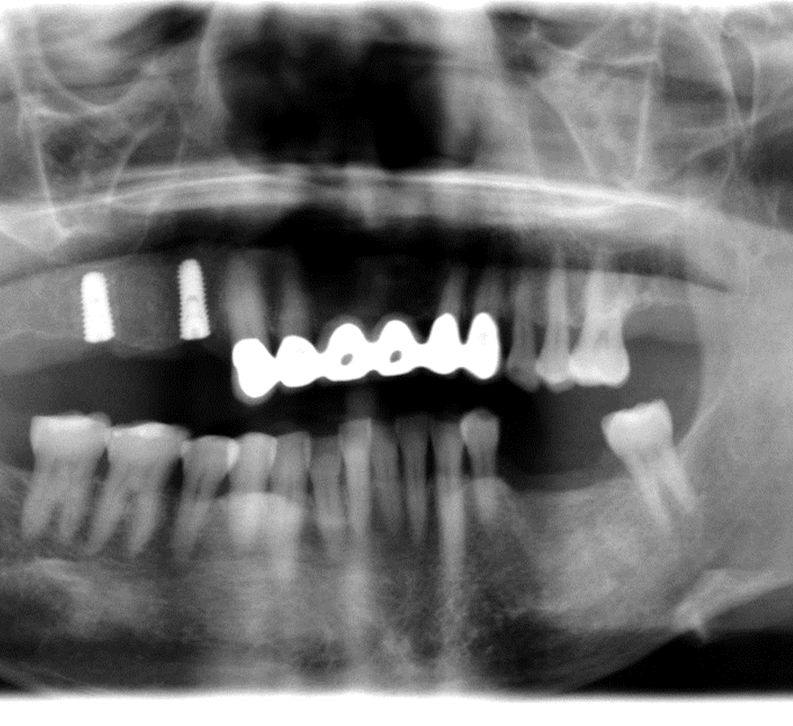
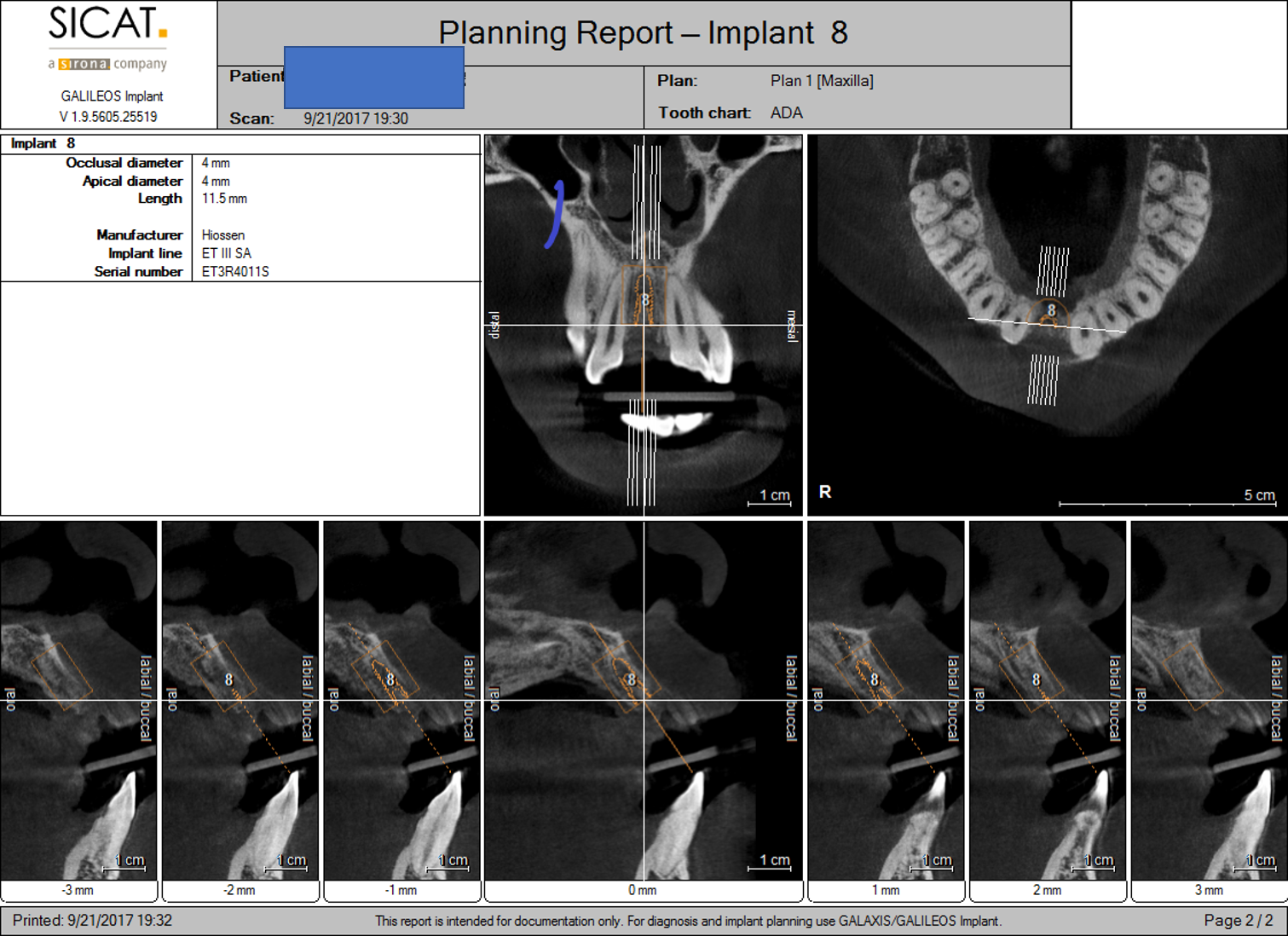
- On site # 3 Shefabone SCPC was used to do indirect sinus lift
- A Osteotomy was created and used to perform the indirect sinus lift with the SCPC then the implant was placed.
- The arrows point to the new bone generated around the dental implanted
- For tooth #5 no graft was used
Case Study 7
Male, 44 yo, no medications or medical conditions.
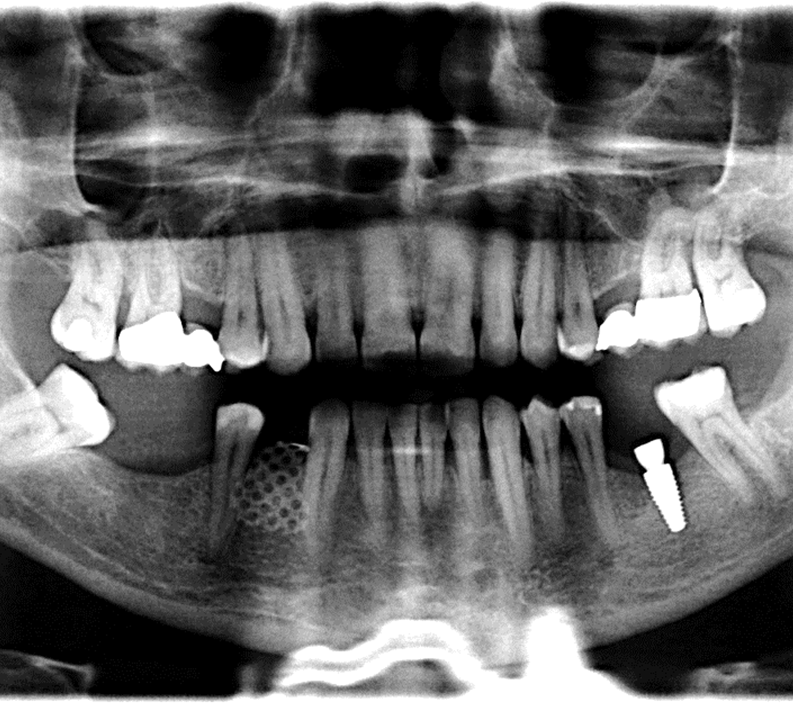
- A resorbed extraction socket (vertical and buccal lingual) resorption of the extraction socket) in site # 28
- The goal was to increase the bone vertical height and thickness.
- Gingival flap to expose the site was made. Cortectomies were made to promote hemorrhaging to have a supply cells and PMP.
- The site was grafted with SCPC particles (on the occlusal and buccal aspects. The Ti mesh was trimmed and placed to cover the grafted site.
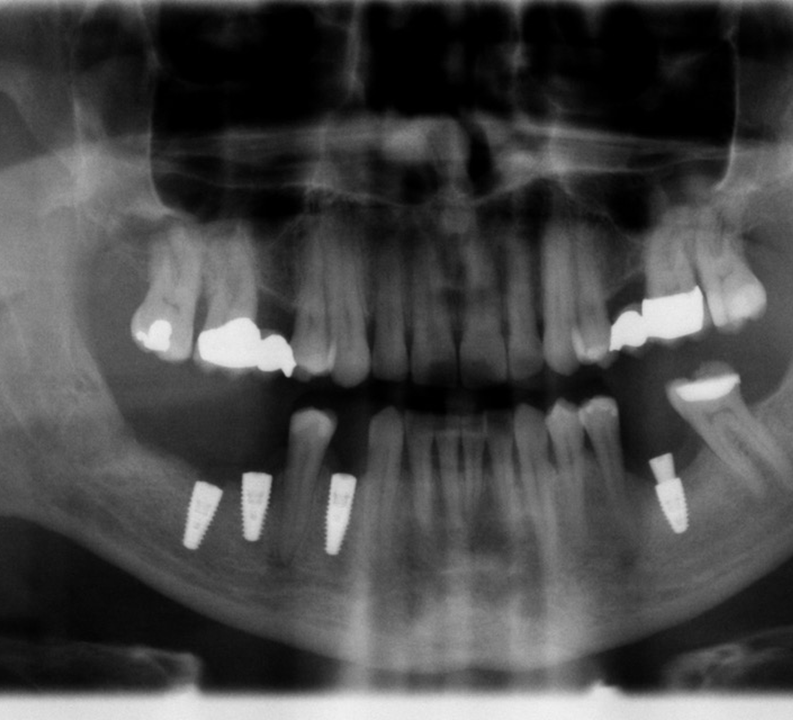
- Radiograph showing the increase in height and buccal lingual dimensions on Site 28 after SCPC grafting for 3 months
- The implant was placed at site # 28
- Bone density and bone quality both were enhanced
Case Study 8
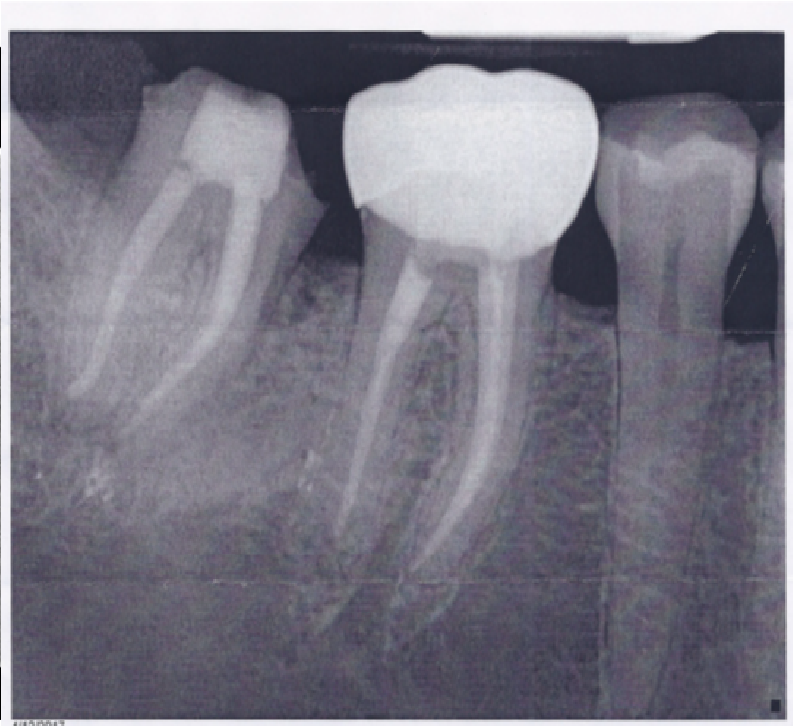
- Preoperative image of fractured tooth # 31 in a 50 yo, female, smoker history, non smoker for 15 years
- Controlled diabetic patient
- Allergy to amexocylin
- She has a vertical root fracture
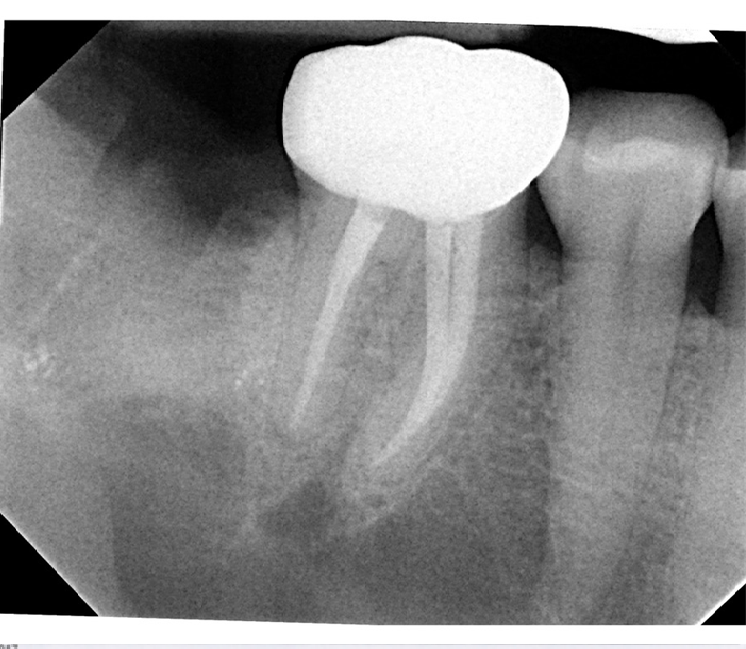
- Radiograph showing the extraction socket of tooth # 31 immediately after grafting with SCPC granules.
- A membrane is placed on top to keep the SCPC granules in place
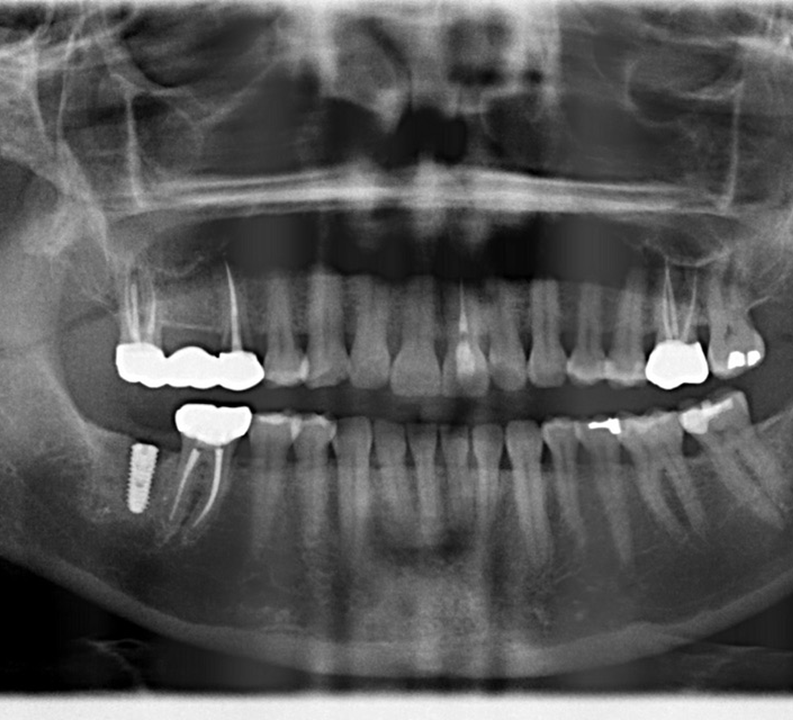
- After 3 months, osteotomy created and the implant was placed at site #31
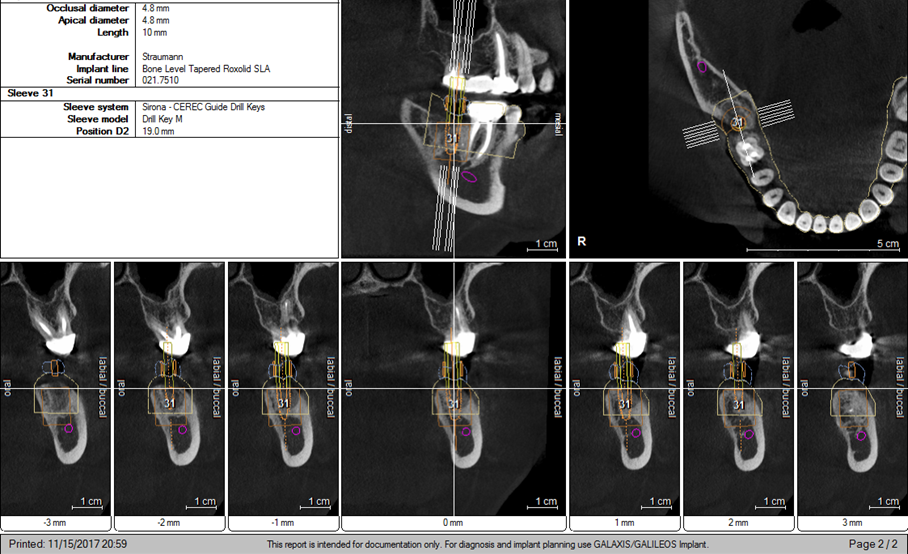
- Implant placed via computer guided procedures.
Case Study 9
‘
Bone Healing 3 Months Postoperative and Implant Stabilization
Case Study 10
Implantation of SCPC into the extraction socket
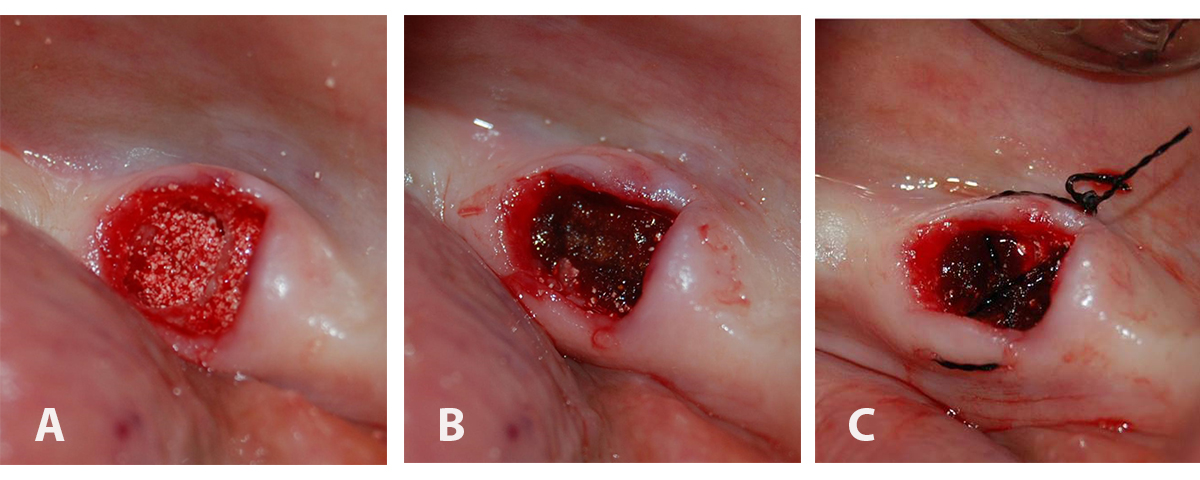
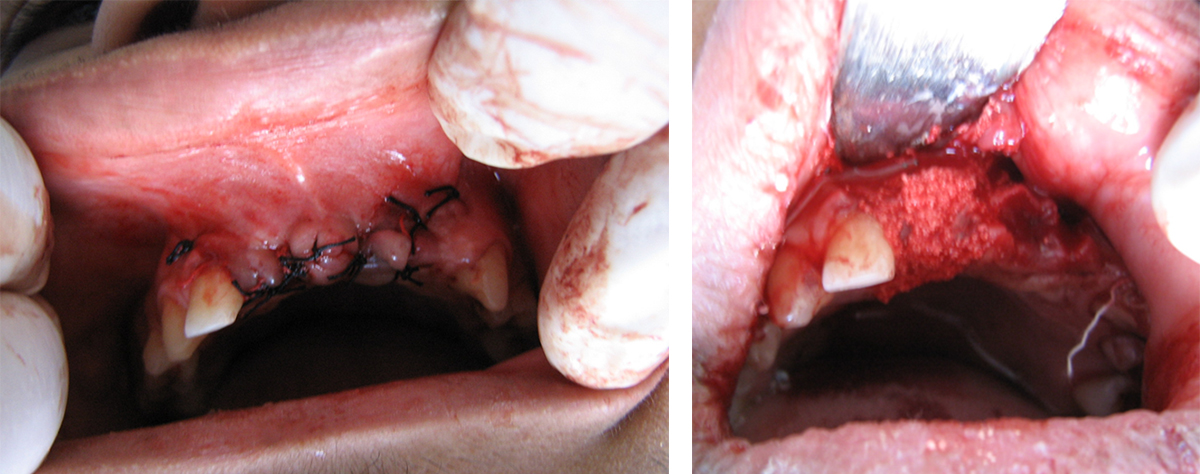
Digital images of (A) the SCPC bone graft granules filling the extraction socket up to crestal bone, (B) gelatin sponge (gelatamp) was placed over the SCPC granules within the extraction socket, and (C) cross mattress suture stabilizes gelatamp in the extraction socket
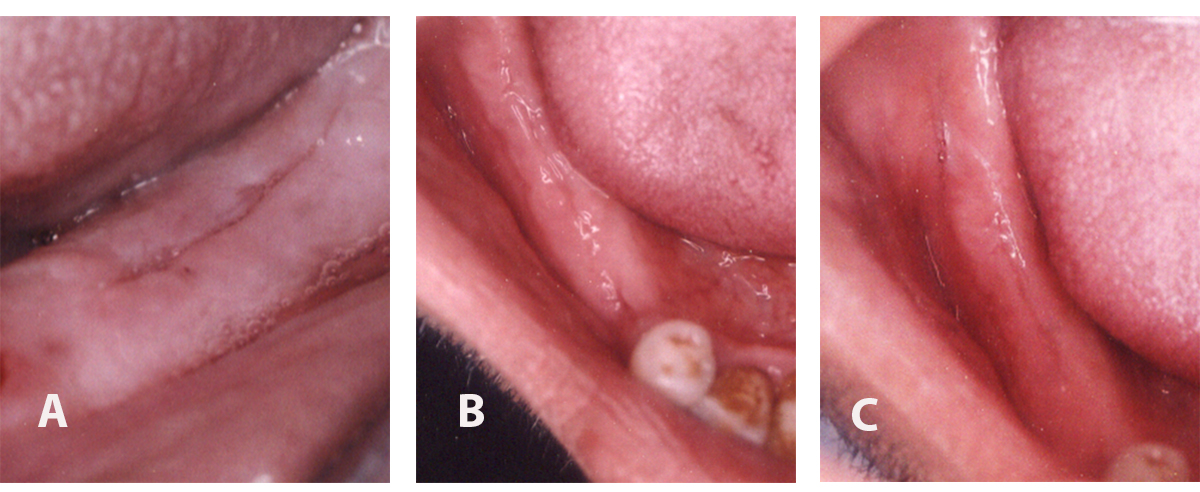
Digital images showing wound healing of the extraction socket grafted with SCPC granules after (A) 2 weeks, (B) 3 months and (C) 6 months postoperatively.
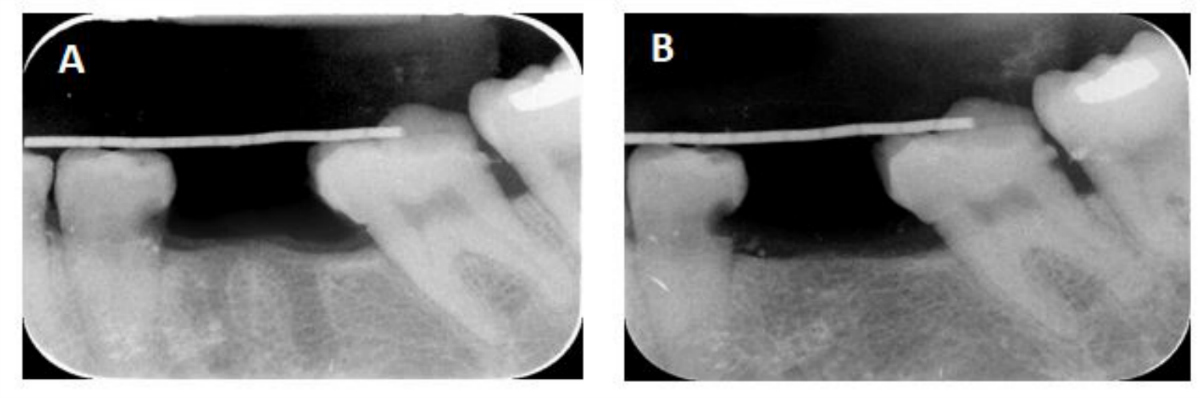
X-ray radiographs showing (A) immediate postoperative image of the extraction sockets and (B) after 6 month, the SCPC grafted sockets were filled with new bone which has comparable radio-opacity to the host bone. Note the complete resorption of the SCPC granules.
Case Study 11
(A) showing two extraction sockets before grafting, (B) the extraction sockets were filled with SCPC granules, (C) Sutured wound after SCPC grafting in the socket.
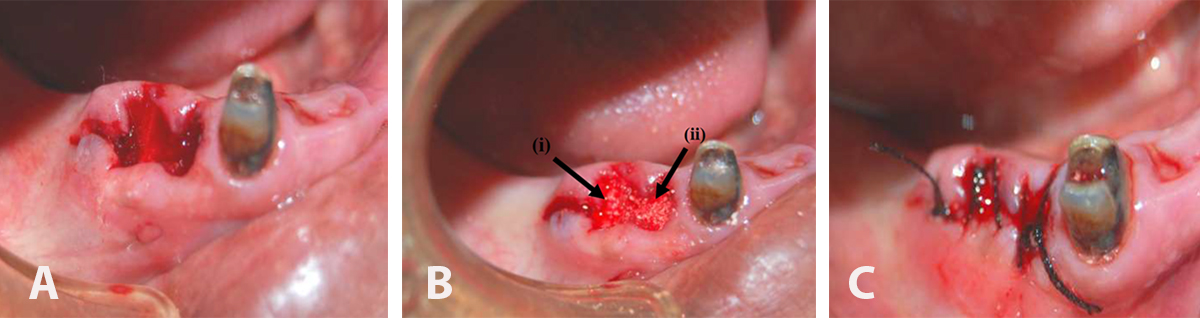
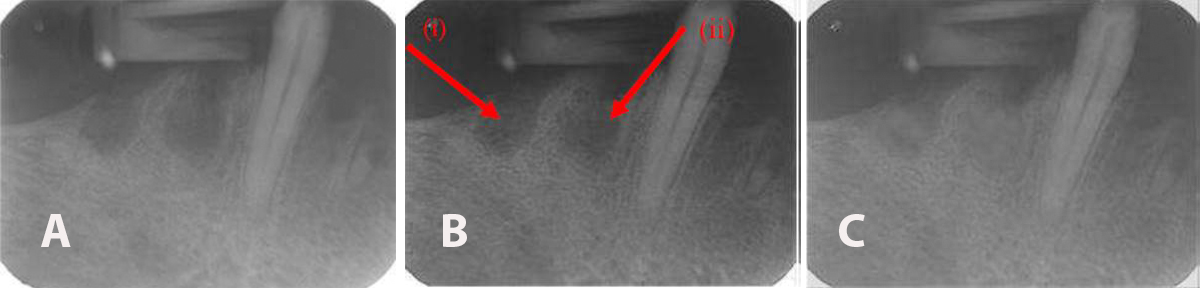
Periapical radiograph showing (A) the extraction sockets before SCPC grafter, (B) two weeks post-grafting SCPC granules showing new bone formation near the walls of the grafted sockets, and (C) After 6 weeks, the radio-opacity inside the grafted sockets became much closer to that of the host bone indicating significant bone formation inside the grafted sockets.
Case Study 12
Photomicrographs of bone biopsy taken from the core of extraction socket grafted with SCPC (for 6 months) at the time of implant insertion. Areas of mature bone with osteons and Haversian system are seen. The resting and reversal lines (yellow arrows) can be seen together with wide thin walled capillaries (green arrows). Areas with woven bone are also present. Sample stained with H&E; magnification 100X.
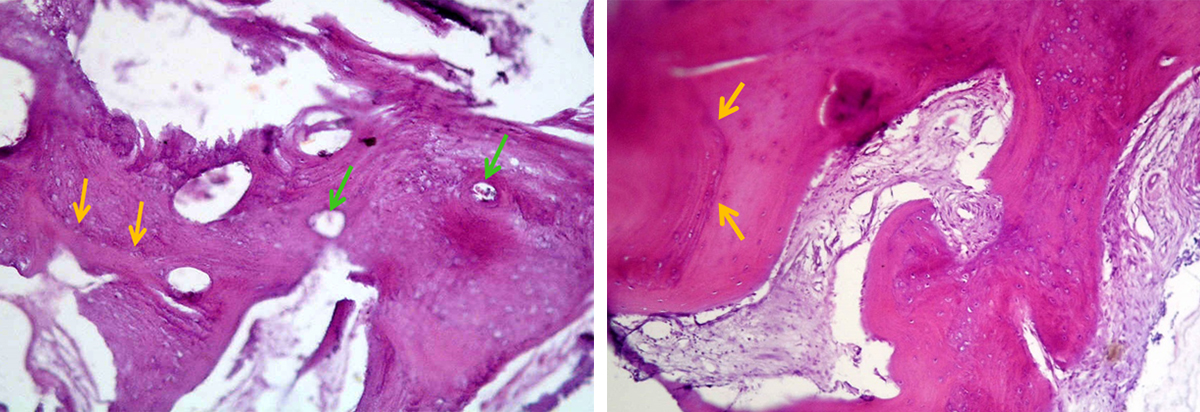
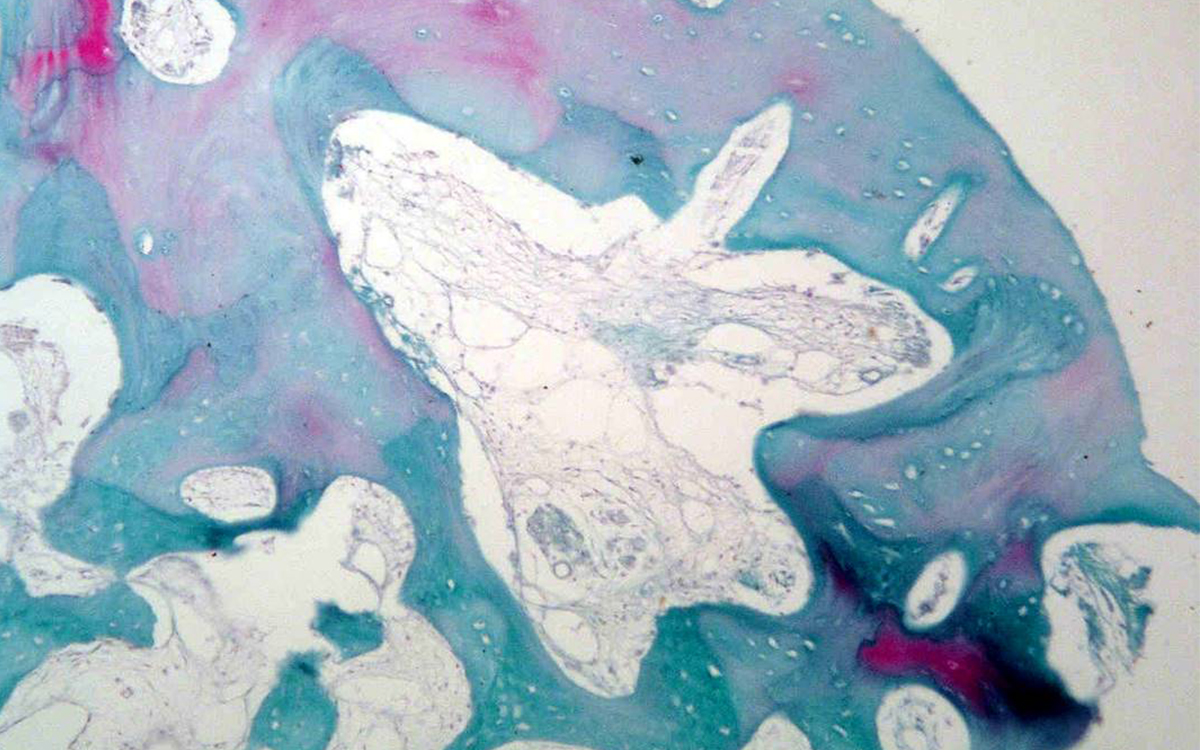
Photomicrograph of bone biopsy taken from extraction socket grafted with SCPC (for 6 months) at the time of implant insertion. Areas of mature bone with osteons and Haversian system are seen together with areas with woven bone. Sample stained with trichrome; magnification 100X.